A Comprehensive Look at the Geographic Map of Mexico
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at the Geographic Map of Mexico
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at the Geographic Map of Mexico. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at the Geographic Map of Mexico

Mexico, a vibrant tapestry of diverse landscapes, cultures, and histories, is a nation whose geographical features play a crucial role in shaping its identity. Understanding Mexico’s geography, through the lens of its map, provides invaluable insight into its physical characteristics, environmental challenges, and economic opportunities.
A Land of Contrasts: The Physical Geography of Mexico
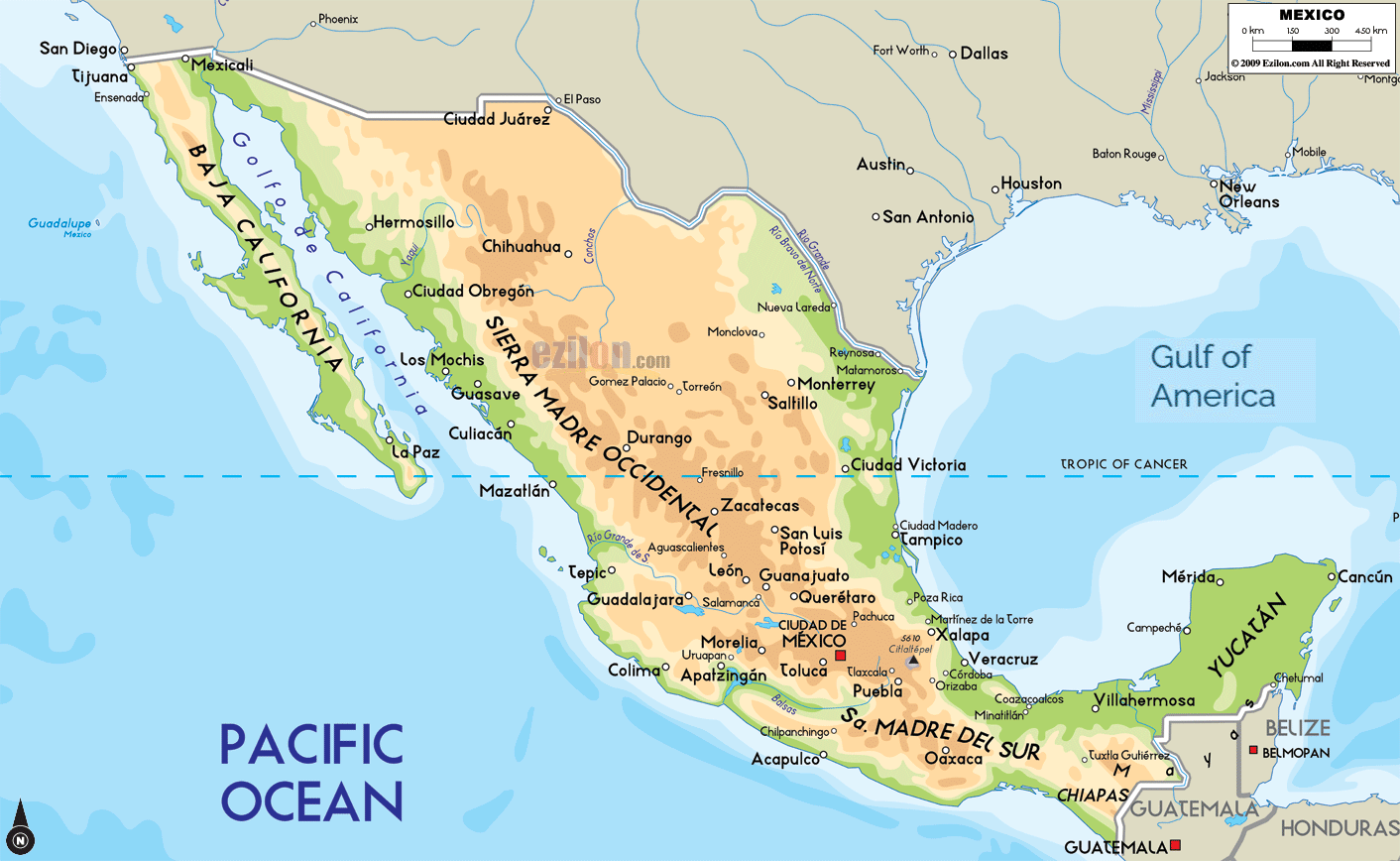
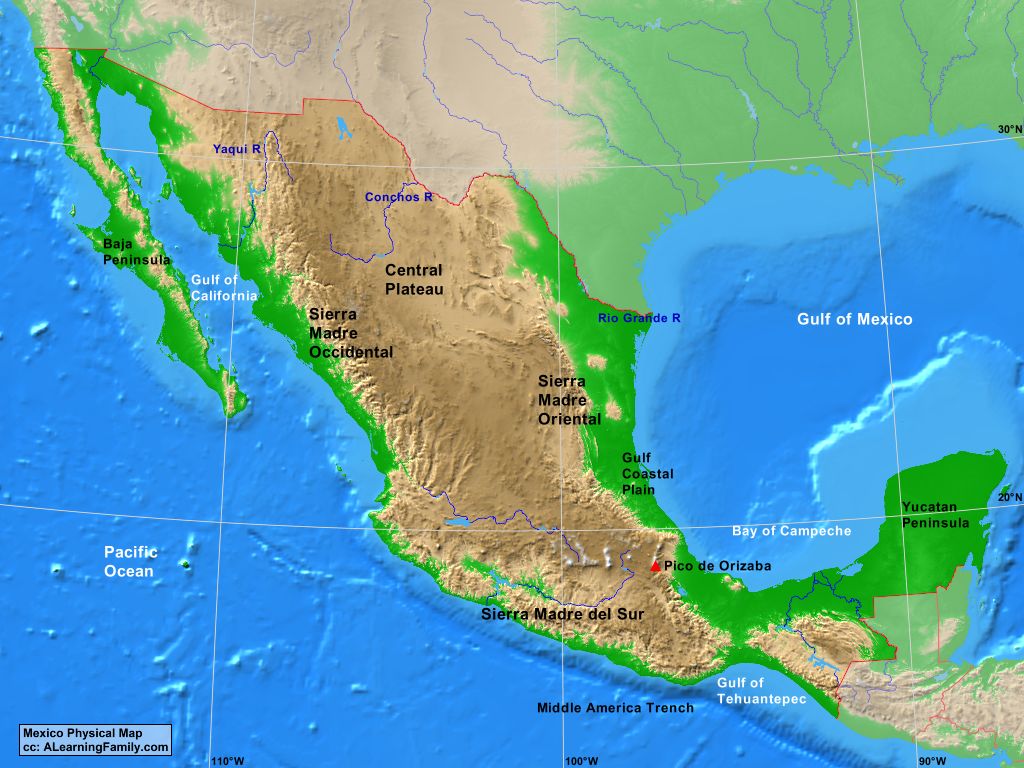
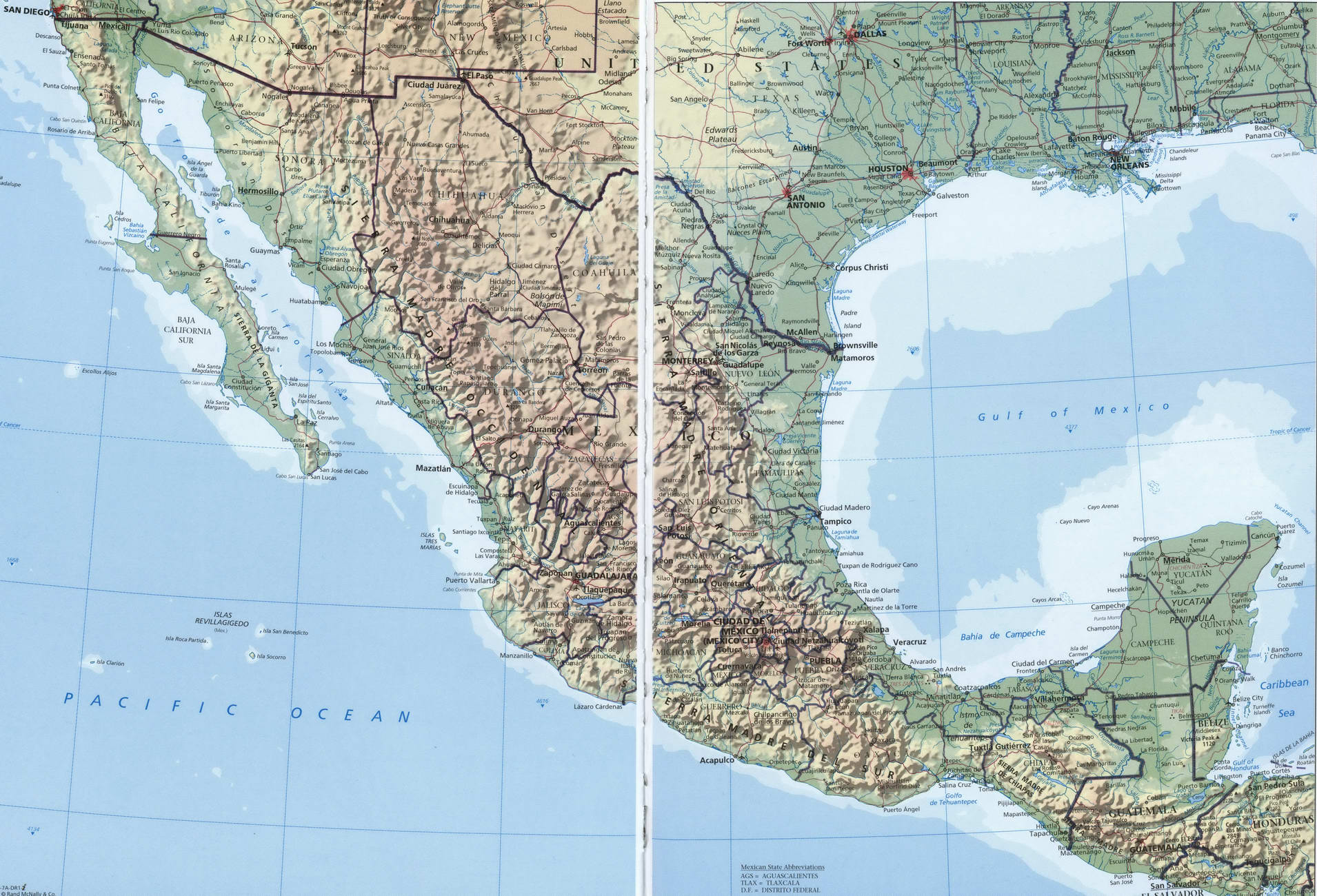
The geographic map of Mexico reveals a country with striking physical diversity. From the towering peaks of the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental to the lush rainforests of the Yucatan Peninsula, Mexico’s landscape presents a captivating array of contrasts.
- The Sierra Madre Mountains: Dominating the western and eastern portions of the country, the Sierra Madre ranges form the backbone of Mexico. These formidable mountains, stretching for thousands of kilometers, are home to diverse ecosystems, including pine forests, grasslands, and deserts.
- The Mexican Plateau: Nestled between the Sierra Madres, the Mexican Plateau is a vast expanse of high-altitude plains and plateaus. This region is characterized by arid and semi-arid climates, with fertile valleys providing fertile ground for agriculture.
- The Coastal Plains: Bordering the Pacific Ocean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean Sea, Mexico’s coastal plains are a vital economic and ecological resource. These lowlands are home to a rich array of ecosystems, including mangroves, beaches, and lagoons, supporting diverse marine life and coastal communities.
- The Yucatan Peninsula: A unique geological formation, the Yucatan Peninsula is a vast, flat limestone plateau. Its distinctive landscape is characterized by cenotes, sinkholes formed by the collapse of limestone bedrock, and a rich biodiversity of flora and fauna.
The Influence of Geography on Mexico’s History and Culture
Mexico’s geographic features have profoundly shaped its history, culture, and development.
- The Influence of Mountains: The Sierra Madre mountains have historically served as natural barriers, isolating communities and contributing to the development of distinct regional cultures. They also played a crucial role in shaping Mexico’s colonial history, providing refuge for indigenous communities resisting Spanish conquest.
- The Importance of Waterways: Mexico’s rivers, lakes, and coastline have been crucial for trade, transportation, and cultural exchange throughout history. The Gulf of Mexico, in particular, has played a vital role in connecting Mexico to the rest of the world.
- The Impact of Climate: Mexico’s diverse climate zones have influenced its agricultural practices, traditional foods, and cultural traditions. The arid climate of the north has shaped the development of drought-resistant crops and livestock herding, while the tropical climate of the south has fostered a rich agricultural diversity.
The Geographic Map as a Tool for Understanding Mexico’s Challenges and Opportunities
The geographic map of Mexico is not merely a static representation of the country’s physical features. It serves as a vital tool for understanding Mexico’s current challenges and opportunities.
- Natural Disasters: Mexico is vulnerable to a range of natural disasters, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, hurricanes, and droughts. The geographic map helps us identify areas at risk and develop mitigation strategies.
- Environmental Challenges: Deforestation, pollution, and climate change are major environmental challenges facing Mexico. The geographic map provides crucial information for understanding the distribution of these problems and developing sustainable solutions.
- Economic Development: Mexico’s geographic location and diverse resources offer significant economic opportunities. The geographic map helps identify areas with potential for agriculture, tourism, and other industries.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Geographic Map of Mexico
1. What are the main geographic regions of Mexico?
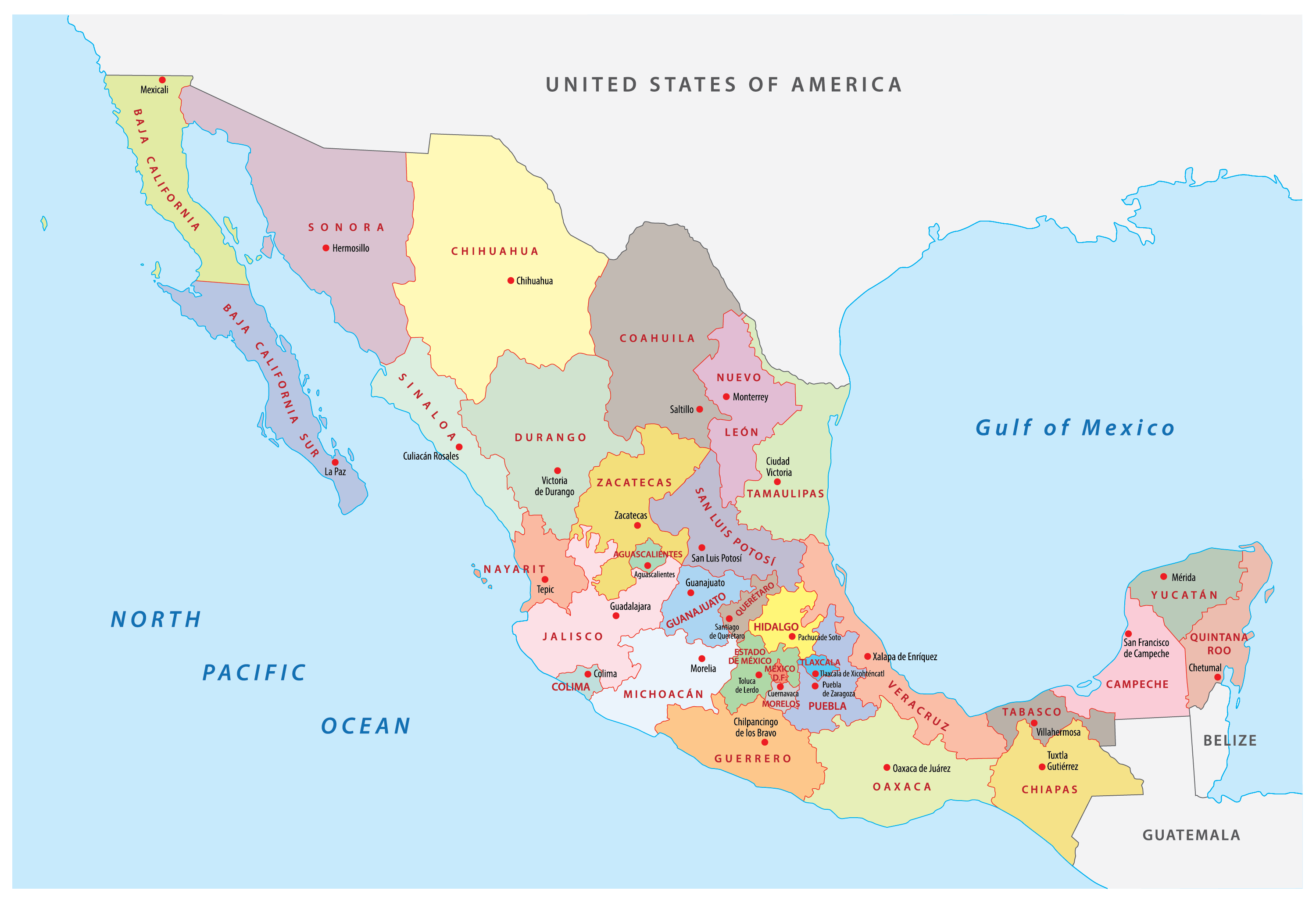
Mexico can be broadly divided into seven geographic regions:
- The North: A vast region characterized by arid and semi-arid climates, the North includes the states of Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo Leon, Tamaulipas, and Durango.
- The Northeast: This region, encompassing the states of Tamaulipas, Nuevo Leon, and Coahuila, is characterized by semi-arid plains and coastal lowlands.
- The Bajio: A fertile region located in central Mexico, the Bajio is known for its agricultural production and historic cities.
- The Center: This region, including the states of Mexico, Morelos, Puebla, and Tlaxcala, is home to Mexico City and other major urban centers.
- The West: This region, encompassing the states of Jalisco, Michoacan, Colima, Nayarit, and Sinaloa, is known for its diverse landscapes, including mountains, coastal plains, and volcanic areas.
- The Southeast: This region, including the states of Veracruz, Oaxaca, Chiapas, and Tabasco, is characterized by tropical rainforests, coastal plains, and mountainous areas.
- The Yucatan Peninsula: This region, encompassing the states of Yucatan, Quintana Roo, and Campeche, is known for its unique geological formation, cenotes, and Mayan archaeological sites.
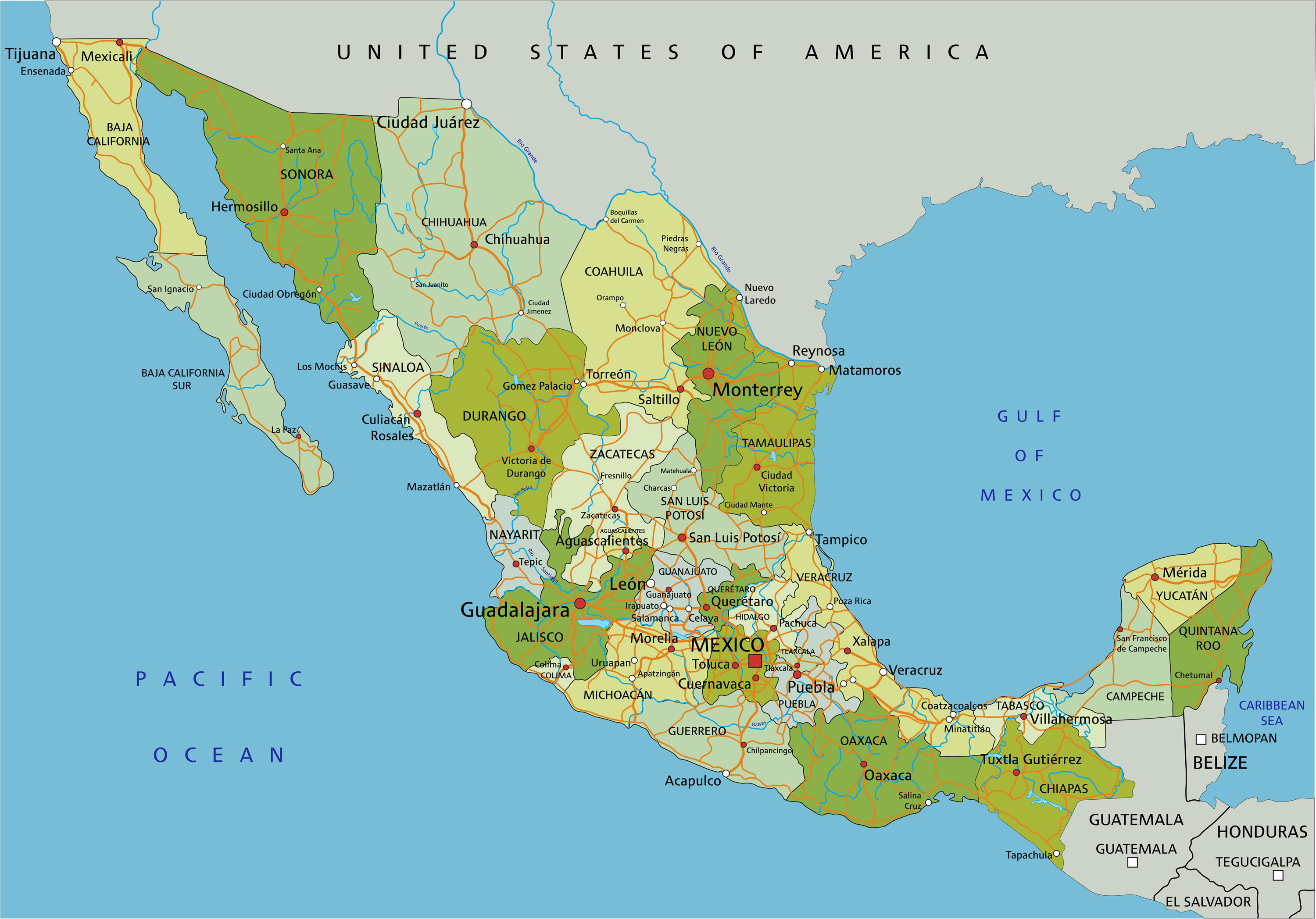
2. What are the major mountain ranges in Mexico?
Mexico is home to three major mountain ranges:
- The Sierra Madre Occidental: This range runs along the western coast of Mexico, from Sonora to Jalisco.
- The Sierra Madre Oriental: This range runs along the eastern coast of Mexico, from Tamaulipas to Veracruz.
- The Sierra Madre del Sur: This range runs along the southern coast of Mexico, from Guerrero to Oaxaca.
3. What are the major rivers in Mexico?
Some of the most important rivers in Mexico include:
- The Rio Grande: This river forms the border between Mexico and the United States.
- The Rio Bravo del Norte: This river is another name for the Rio Grande.
- The Rio Balsas: This river flows through the central and southern parts of Mexico.
- The Rio Usumacinta: This river flows through the southern part of Mexico, forming the border between Mexico and Guatemala.
4. What are the major lakes in Mexico?
Mexico is home to several important lakes, including:
- Lake Chapala: This lake is the largest lake in Mexico.
- Lake Catemaco: This lake is known for its beautiful scenery and diverse wildlife.
- Lake Xochimilco: This lake is located in Mexico City and is known for its canals and traditional trajineras (boats).
5. What are the major cities in Mexico?
Some of the largest and most important cities in Mexico include:
- Mexico City: The capital of Mexico, Mexico City is the largest city in North America.
- Guadalajara: The second-largest city in Mexico, Guadalajara is located in the state of Jalisco.
- Monterrey: The third-largest city in Mexico, Monterrey is located in the state of Nuevo Leon.
- Tijuana: This city is located on the border with the United States and is a major center for trade and tourism.
- Cancun: This city is located on the Yucatan Peninsula and is a popular tourist destination.
Tips for Understanding the Geographic Map of Mexico
- Use a variety of resources: Explore physical maps, online maps, and satellite imagery to gain a comprehensive understanding of Mexico’s geography.
- Focus on key features: Pay attention to the major mountain ranges, rivers, lakes, and cities.
- Consider the impact of geography on human activity: Think about how Mexico’s geography has shaped its history, culture, and economy.
- Connect the dots: Use the geographic map to understand the relationships between different regions of Mexico and the challenges and opportunities they face.
Conclusion
The geographic map of Mexico is a powerful tool for understanding this complex and fascinating country. By examining its physical features, climate zones, and historical development, we gain a deeper appreciation for the unique tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and challenges that make up Mexico. As we navigate the complexities of the 21st century, understanding Mexico’s geography will be crucial for addressing its environmental challenges, fostering economic growth, and promoting sustainable development.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at the Geographic Map of Mexico. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!