Charting the Frontier: A Journey Through the Map of Alta California
Related Articles: Charting the Frontier: A Journey Through the Map of Alta California
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Charting the Frontier: A Journey Through the Map of Alta California. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Frontier: A Journey Through the Map of Alta California

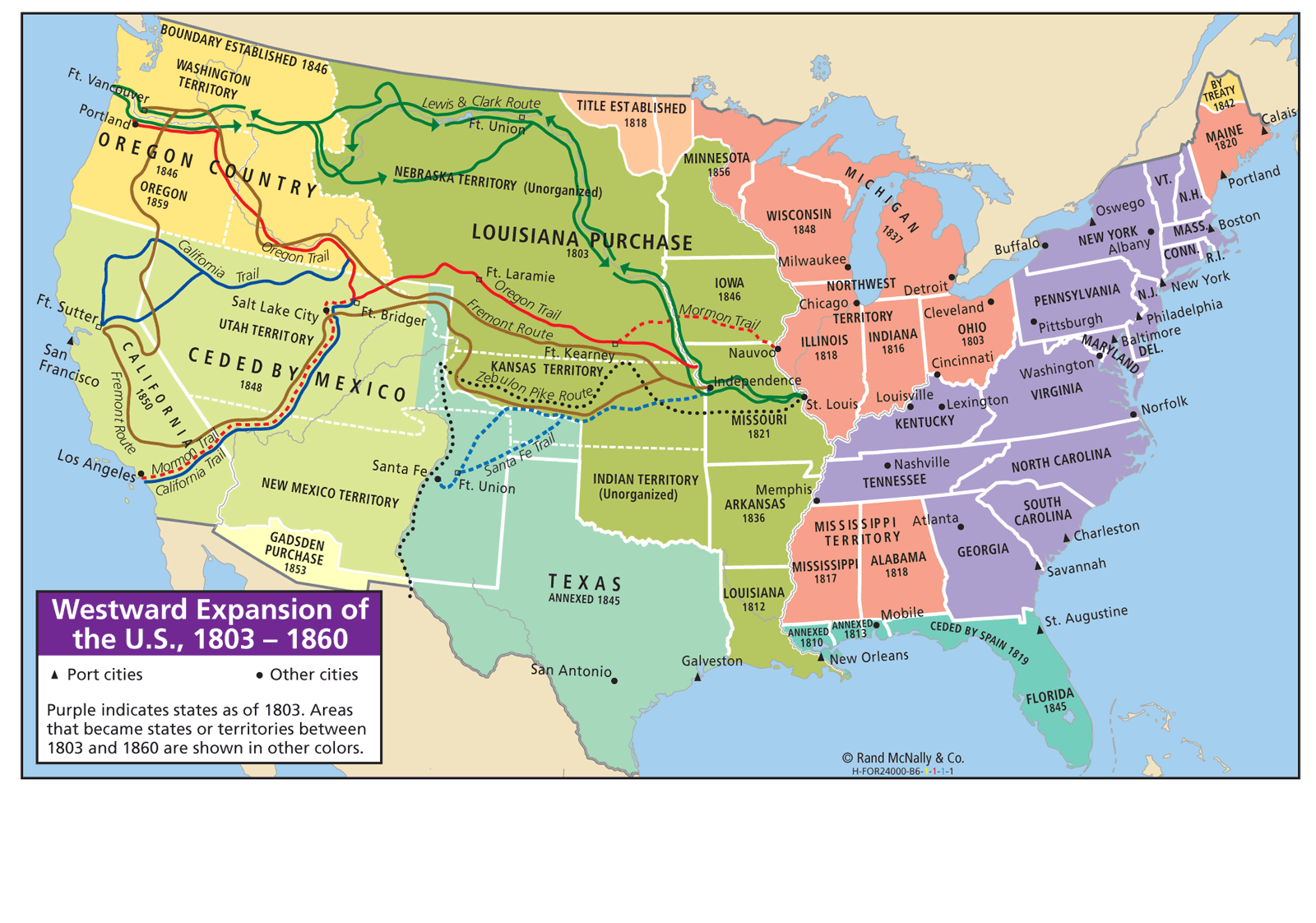
The map of Alta California, encompassing the vast expanse of land that spanned from present-day Oregon to Baja California, serves as a captivating window into a pivotal period of North American history. This region, once a Spanish colony, witnessed a dynamic interplay of indigenous cultures, European exploration, and the eventual emergence of a new nation. Understanding the map of Alta California, its features, and its significance, allows us to delve into a rich tapestry of events that shaped the American West.
A Land of Contrasts: Delving into the Geographical Landscape
The map of Alta California reveals a diverse landscape, characterized by rugged mountains, fertile valleys, and a sprawling coastline. The towering Sierra Nevada range, a defining feature of the region, served as a natural barrier, influencing the flow of people and resources. The Central Valley, a fertile expanse nestled between the Sierra Nevada and the Coast Ranges, provided ample land for agriculture and became a vital economic hub.
The Pacific Ocean, with its vast expanse and abundant resources, offered opportunities for fishing, trade, and exploration. The coastline, dotted with natural harbors and bays, facilitated maritime commerce and provided strategic locations for settlements. The diverse topography of Alta California presented both challenges and opportunities, shaping the lives of its inhabitants and influencing its historical development.
A Tapestry of Cultures: Indigenous Peoples and Spanish Colonization
Prior to the arrival of Europeans, Alta California was home to a diverse array of indigenous cultures. The Chumash, Miwok, and Salinan peoples, among others, had established thriving communities and developed sophisticated social structures, languages, and traditions. Their lives were intricately intertwined with the land, and they possessed a deep understanding of the natural world.
Spanish colonization, beginning in the late 18th century, profoundly impacted the indigenous inhabitants of Alta California. The arrival of Spanish explorers, missionaries, and settlers led to the establishment of missions, presidios, and pueblos, marking the introduction of European culture and governance. This interaction resulted in a complex and often fraught relationship between indigenous communities and the Spanish colonizers.
The Rise of California Ranchos: A Legacy of Land Ownership
The Spanish land grant system, which granted large tracts of land to individuals and families, played a crucial role in shaping the social and economic landscape of Alta California. These land grants, known as ranchos, became the foundation of a sprawling cattle ranching economy, influencing the development of the region and leaving a lasting legacy on the ownership of land in California.
The ranchos, with their vast expanses of land and their emphasis on cattle raising, contributed to the development of a distinct culture and way of life in Alta California. They fostered a sense of independence and self-reliance among the Californios, the Spanish-speaking inhabitants of the region, and played a significant role in shaping the social fabric of the area.
The Mexican Era: A Period of Transition
Following Mexico’s independence from Spain in 1821, Alta California became part of the newly formed Mexican Republic. This period witnessed significant changes in the region, as Mexican governance replaced Spanish rule. The Mexican government encouraged settlement and economic development, leading to increased immigration and a growing population.
The Mexican era also saw the emergence of new political and social dynamics in Alta California. The Californios, now citizens of Mexico, played an active role in local governance and contributed to the development of a distinctive Californian identity. However, tensions between the Californios and the Mexican government, along with growing American influence, ultimately led to the Mexican-American War.
The American Conquest and the Birth of a New State
The Mexican-American War, fought from 1846 to 1848, resulted in the cession of Alta California to the United States. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, signed in 1848, officially transferred ownership of the vast territory to the United States, marking a significant turning point in the history of the region.
The American conquest of Alta California brought about profound changes in the social, political, and economic landscape. The arrival of American settlers, driven by the promise of land and opportunity, led to a rapid influx of new residents. The gold rush of 1849, which drew thousands of prospectors to the region, further fueled population growth and economic transformation.
The Legacy of Alta California: Shaping the American West
The map of Alta California, with its intricate tapestry of cultures, its vast geographical expanse, and its turbulent history, provides a compelling narrative of the American West. The region’s indigenous inhabitants, the Spanish colonists, and the Mexican government each played a pivotal role in shaping its destiny. The American conquest, followed by the gold rush, ushered in a new era of development and transformed Alta California into the vibrant and dynamic state of California.
The legacy of Alta California continues to resonate today, influencing the culture, economy, and identity of the state. From its diverse landscape to its rich history, California stands as a testament to the transformative power of migration, conquest, and the enduring spirit of its people.
FAQs
Q: What were the major geographical features of Alta California?
A: Alta California was characterized by a diverse landscape, including the towering Sierra Nevada range, the fertile Central Valley, and a sprawling coastline dotted with natural harbors and bays.
Q: Who were the indigenous inhabitants of Alta California?
A: Alta California was home to a diverse array of indigenous cultures, including the Chumash, Miwok, and Salinan peoples, who had established thriving communities and developed sophisticated social structures, languages, and traditions.
Q: What was the impact of Spanish colonization on Alta California?
A: Spanish colonization led to the establishment of missions, presidios, and pueblos, introducing European culture and governance and profoundly impacting the indigenous inhabitants.
Q: What were the major features of the rancho system?
A: The Spanish land grant system, which granted large tracts of land to individuals and families, played a crucial role in shaping the social and economic landscape of Alta California, leading to the development of a sprawling cattle ranching economy.
Q: What were the key events of the Mexican era in Alta California?
A: The Mexican era witnessed significant changes in governance, increased immigration, and the emergence of new political and social dynamics, but tensions between the Californios and the Mexican government ultimately led to the Mexican-American War.
Q: What were the consequences of the American conquest of Alta California?
A: The American conquest brought about profound changes, including a rapid influx of American settlers, the gold rush, and the transformation of Alta California into the vibrant state of California.
Tips
- Visualize the map: Use online maps or historical maps to gain a better understanding of the geographical features and locations of Alta California.
- Research the indigenous cultures: Explore the history, traditions, and languages of the indigenous peoples who inhabited Alta California.
- Learn about the rancho system: Understand the impact of the Spanish land grant system on the social and economic development of the region.
- Study the Mexican era: Research the political, social, and economic changes that occurred during this period.
- Explore the American conquest and the gold rush: Investigate the consequences of these events on the transformation of Alta California.
Conclusion
The map of Alta California offers a compelling glimpse into a pivotal period of American history, showcasing the dynamic interplay of cultures, the impact of colonization, and the emergence of a new state. By understanding the geographical features, the indigenous inhabitants, the Spanish and Mexican eras, and the American conquest, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of events that shaped the American West and left an enduring legacy on the state of California. The map of Alta California serves as a reminder of the complex and fascinating history of a region that continues to captivate and inspire.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Frontier: A Journey Through the Map of Alta California. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!