Deciphering the Geography of Northern France: A Regional Analysis
Related Articles: Deciphering the Geography of Northern France: A Regional Analysis
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Geography of Northern France: A Regional Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Geography of Northern France: A Regional Analysis

Northern France, a region encompassing a diverse array of landscapes and historical significance, presents a complex geographical tapestry. Understanding this area necessitates a detailed examination of its physical features, administrative divisions, and the interplay between its geography and historical development. Analyzing this region through cartographic representation reveals crucial insights into its economic activities, cultural heritage, and strategic importance.
Physical Geography: A Foundation for Understanding
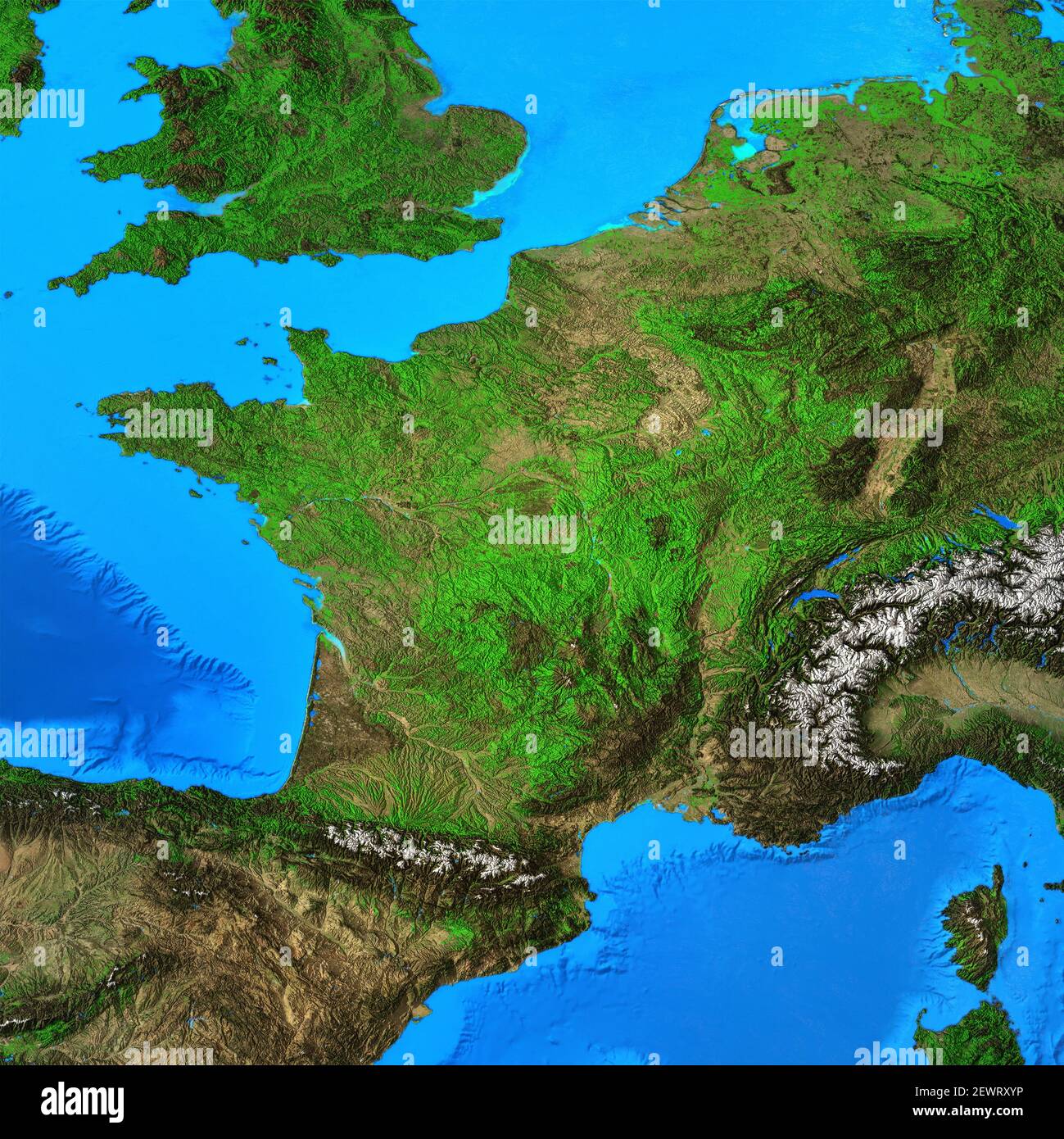
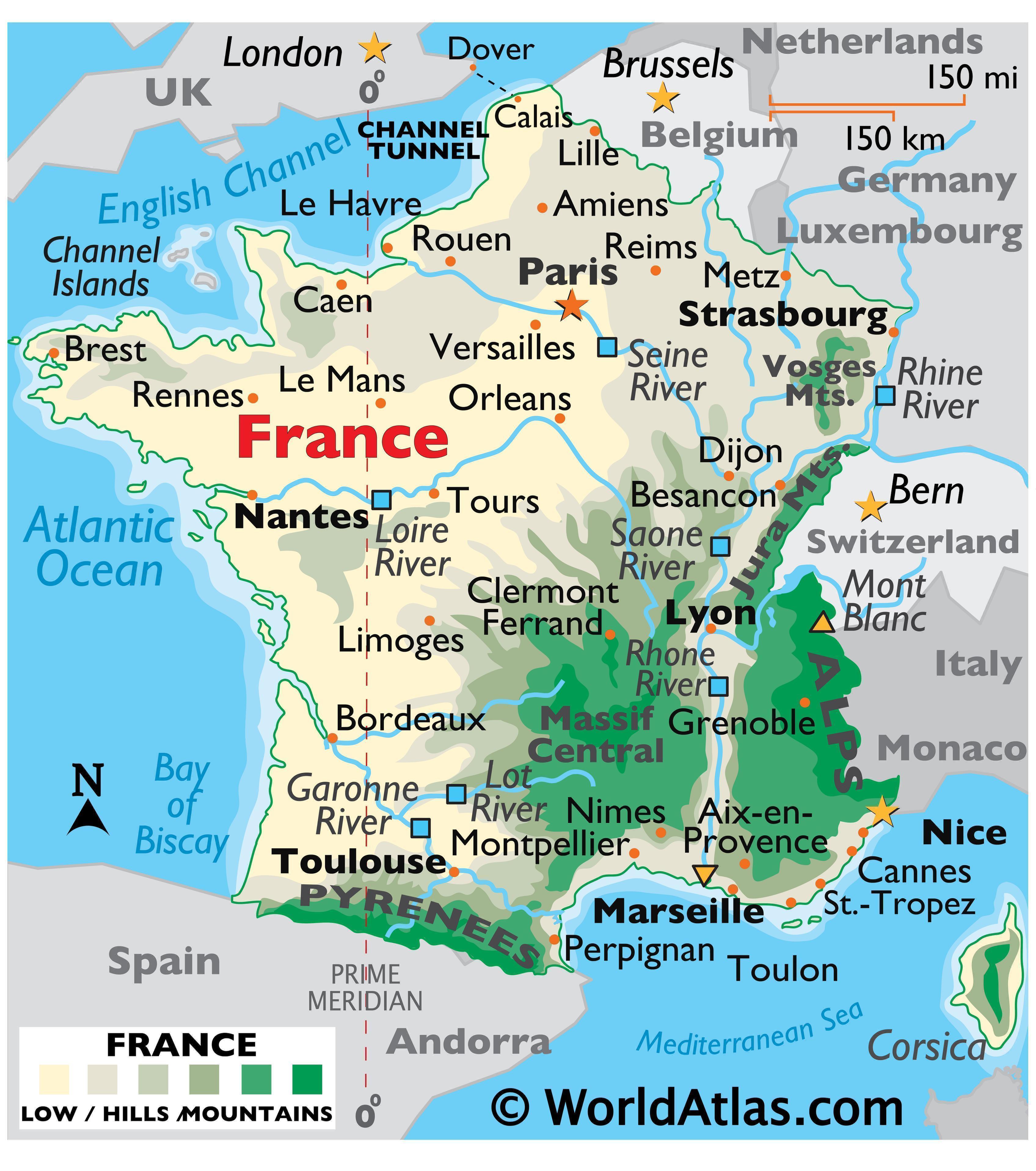
The region’s topography is characterized by significant variations. The northernmost parts are predominantly flat, comprising the fertile plains of the Paris Basin, ideal for agriculture. This area, extending towards the Channel coast, features extensive arable land, supporting intensive farming practices and contributing significantly to France’s agricultural output. The coastline itself is remarkably diverse, ranging from the sandy beaches of Normandy to the dramatic cliffs of the Pas-de-Calais. These coastal areas have historically played crucial roles in trade and defense.
Moving inland, the landscape gradually transitions towards rolling hills and low-lying plateaus. This area is interspersed with river valleys, notably those of the Seine, Somme, and Scheldt, which have served as vital transportation arteries throughout history. These rivers have facilitated trade, communication, and the development of settlements along their banks. The Ardennes region, located in the southeast of Northern France, stands in contrast to the flatter north. This area is characterized by a more rugged terrain, featuring hills and forests, impacting settlement patterns and economic activities.
The region’s climate is temperate maritime, influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and the English Channel. This results in relatively mild winters and cool summers, providing favorable conditions for agriculture and supporting a variety of ecosystems. However, the region is also susceptible to occasional severe weather events, including storms and flooding, which necessitate careful planning and infrastructure development.
Administrative Divisions and Regional Identity
Northern France is not a single administrative unit but encompasses several regions and departments. These divisions, often reflecting historical boundaries and regional identities, play a crucial role in governance, economic planning, and cultural expression. The regions of Hauts-de-France and Normandy, for example, each possess unique characteristics and historical legacies, influencing their respective economic development and cultural landscapes. Understanding these administrative divisions is essential for interpreting regional variations in population density, economic activity, and infrastructure development.
Historical Significance and Strategic Importance
The geography of Northern France has profoundly shaped its history and continues to influence its strategic importance. Its proximity to the English Channel has made it a pivotal point of contention throughout centuries, resulting in numerous battles and conflicts. The coastal areas have served as both invasion routes and defensive positions, leaving a rich tapestry of historical sites and battlefields. The region’s strategic location, bordering Belgium and the United Kingdom, has also played a crucial role in international relations and trade.
The fertile plains of the Paris Basin have supported large populations and fostered the development of major cities, contributing to the region’s economic and political influence. The network of rivers and canals has facilitated trade and communication, connecting Northern France to other parts of the country and Europe. This intricate interplay between geography and history has shaped the region’s cultural identity and its ongoing development.
Economic Activities and Infrastructure
The geography of Northern France underpins its diverse economic activities. Agriculture, particularly the cultivation of grains and dairy farming, remains a significant sector in the fertile plains. The coastal areas support fishing and related industries. Furthermore, the region’s strategic location and well-developed infrastructure have fostered industrial development, particularly in areas such as automotive manufacturing and logistics. Major ports, such as Le Havre and Dunkirk, serve as crucial gateways for international trade. The region’s network of highways, railways, and canals facilitates the movement of goods and people, underpinning its economic dynamism.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are the major geographical features of Northern France? The region encompasses the fertile plains of the Paris Basin, the coastline of the English Channel and North Sea, the rolling hills and plateaus of inland areas, and the more rugged terrain of the Ardennes.
-
How has the geography of Northern France influenced its history? Its proximity to the English Channel has made it a focal point of conflict, while the fertile plains have supported large populations and economic development. The river systems have facilitated trade and communication.
-
What are the major economic activities in Northern France? Agriculture, fishing, industry (particularly automotive and logistics), and tourism are prominent economic sectors.
-
What are the main administrative divisions of Northern France? The region is divided into several departments and regions, including Hauts-de-France and Normandy, each with its own unique characteristics.
-
What are the key challenges faced by Northern France due to its geography? The region is susceptible to severe weather events, such as storms and flooding. Maintaining and improving infrastructure in diverse geographical areas presents ongoing challenges.
Tips for Understanding the Geography of Northern France:
- Utilize detailed topographical maps to grasp the variations in elevation and landscape features.
- Consult historical maps to understand the evolution of settlement patterns and land use.
- Explore online resources and geographical information systems (GIS) data to obtain comprehensive information.
- Consider the influence of climate on agriculture and other economic activities.
- Analyze the role of transportation infrastructure in connecting different parts of the region.
Conclusion:
The geography of Northern France is a complex and multifaceted element, deeply intertwined with its history, culture, and economic development. Understanding its physical features, administrative divisions, and historical significance provides crucial context for interpreting the region’s present and future trajectory. By analyzing cartographic representations and considering the interplay between geography and human activity, a comprehensive understanding of this vital region can be achieved. Further research into specific aspects, such as the impact of climate change or the evolution of urban centers, can enrich this understanding even further.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Geography of Northern France: A Regional Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!