Decoding Utah’s Topography: An Analysis of Elevation Data
Related Articles: Decoding Utah’s Topography: An Analysis of Elevation Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Decoding Utah’s Topography: An Analysis of Elevation Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding Utah’s Topography: An Analysis of Elevation Data
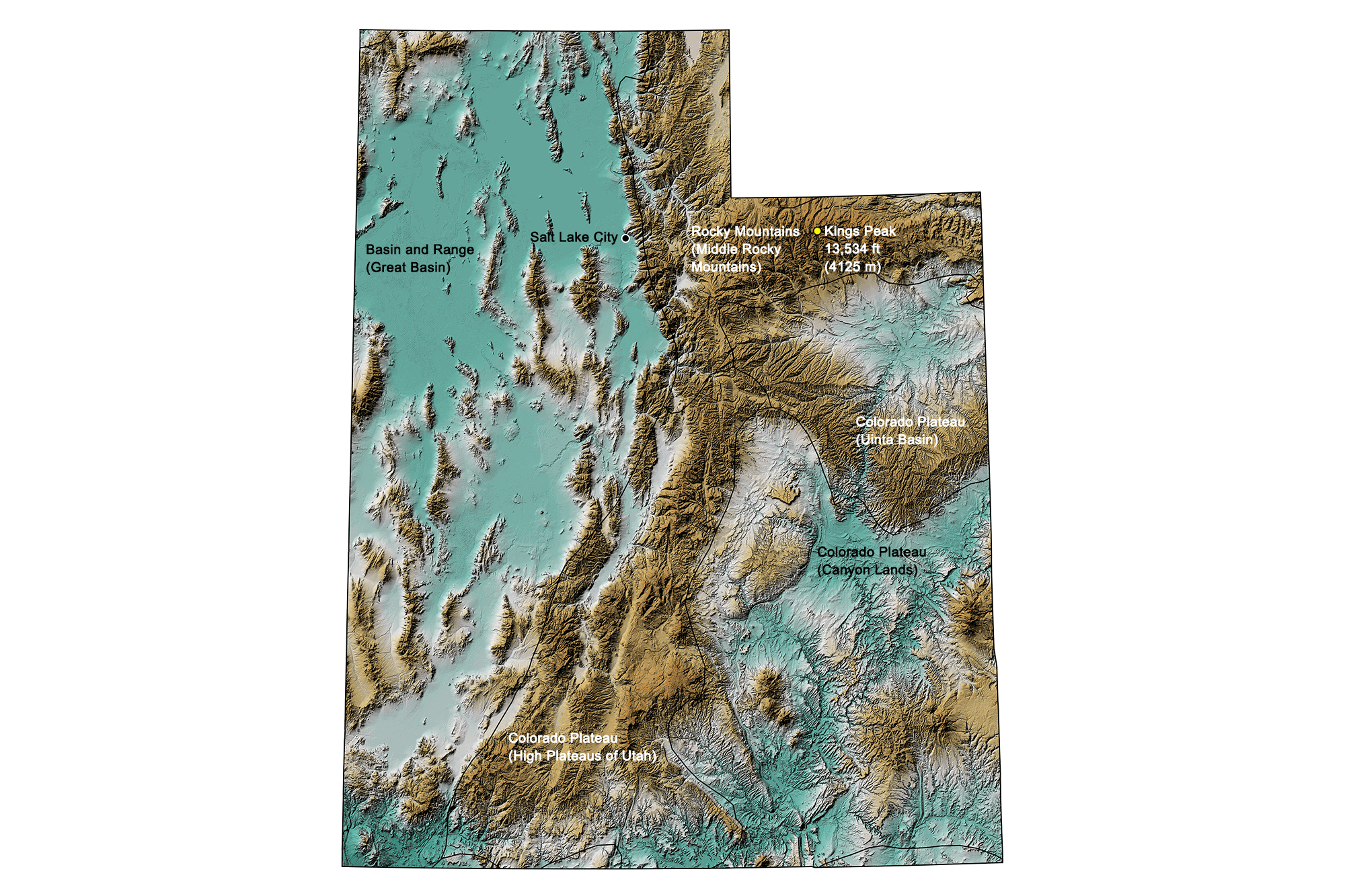
Utah’s dramatic landscape, a tapestry woven from towering mountains, deep canyons, and expansive deserts, is vividly portrayed through its elevation data. This geographical information, typically visualized as a topographic map, offers invaluable insights into the state’s diverse ecosystems, geological formations, and human development patterns. Understanding this data is crucial for a multitude of applications, ranging from resource management and infrastructure planning to environmental conservation and recreational activities.
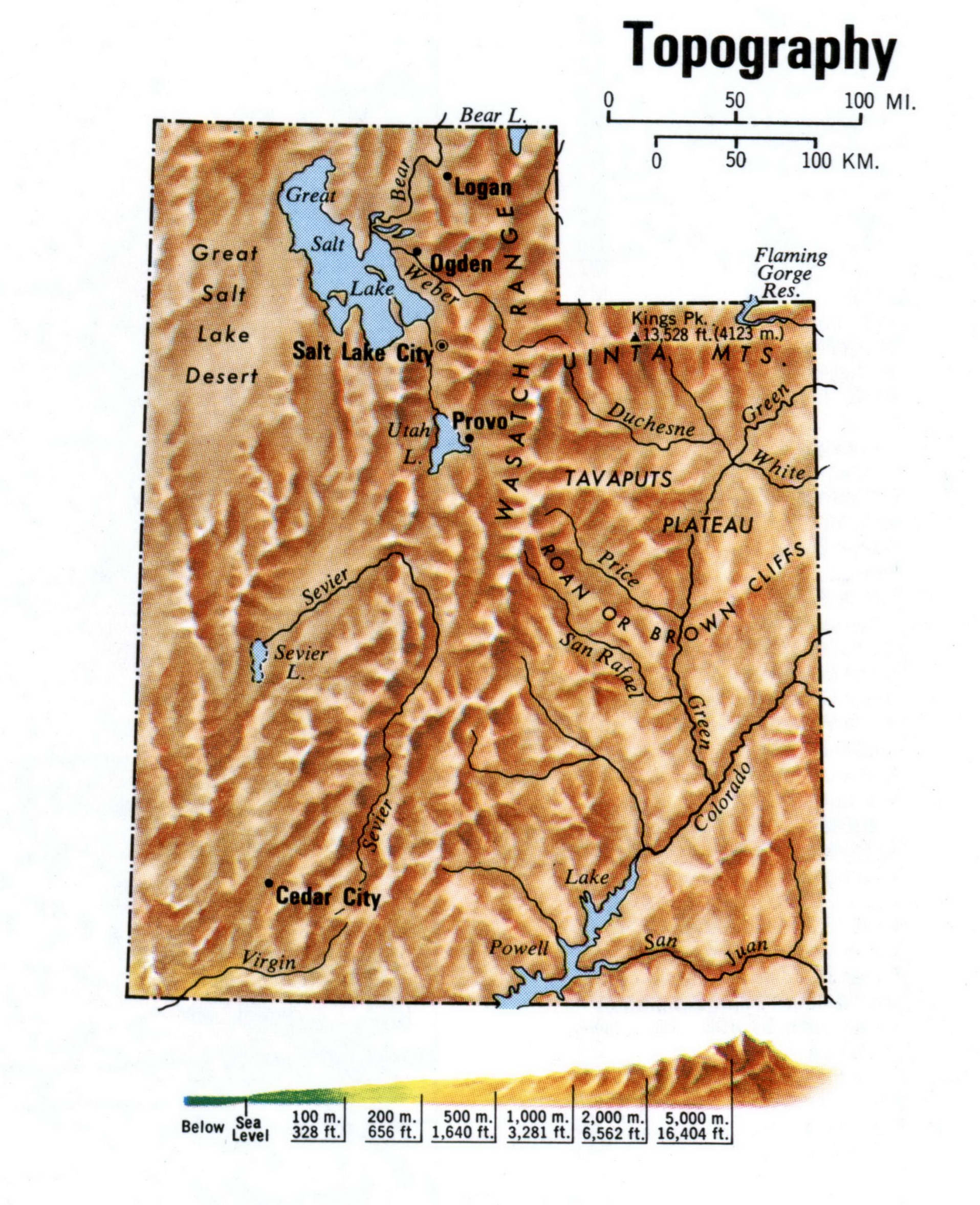
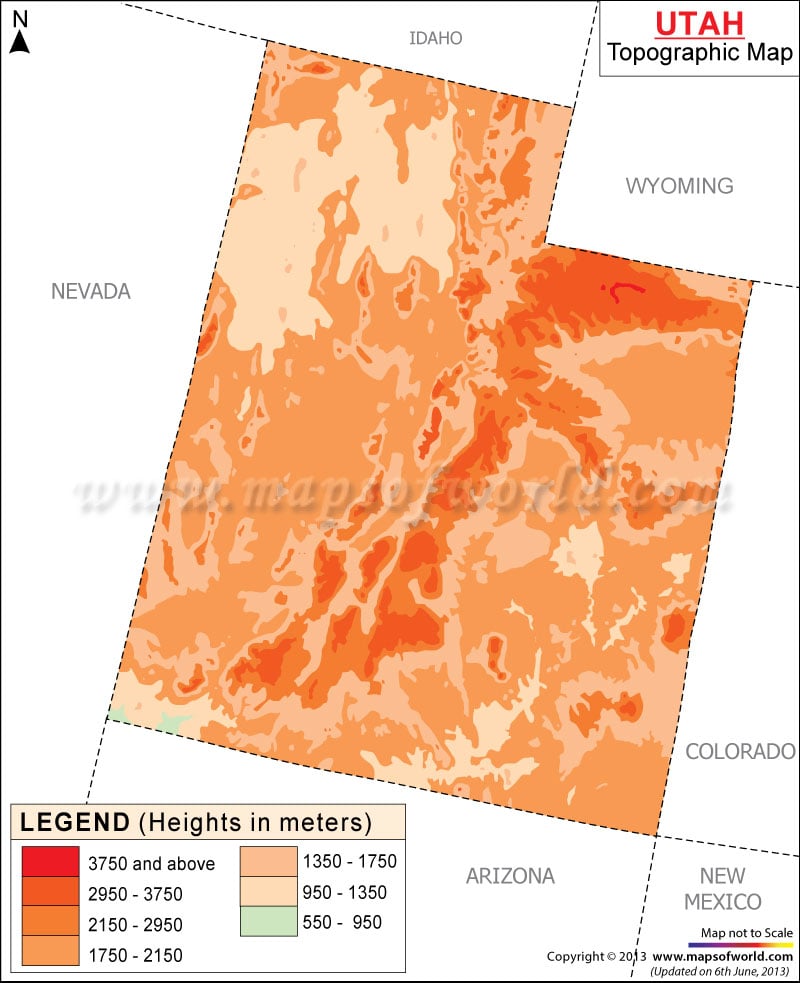
The state’s elevation varies dramatically, ranging from the lowest point at 2,500 feet above sea level in Beaver County along the Colorado River to the highest peak, Kings Peak in the Uinta Mountains, reaching over 13,500 feet. This significant elevation gradient results in a diverse array of microclimates, impacting vegetation, animal populations, and human settlement patterns. The Wasatch Range, a prominent north-south mountain chain, acts as a significant hydrological divide, influencing precipitation patterns and the flow of rivers and streams. The Great Basin, occupying a large portion of western Utah, is characterized by its internal drainage, with numerous endorheic basins and salt flats. These geographical features are clearly delineated on elevation maps, providing a visual representation of the complex interplay of geological processes that have shaped the state’s topography.
Elevation data is fundamental for several key applications. Hydrological modeling, for instance, relies heavily on accurate elevation information to simulate water flow, predict flood risks, and manage water resources effectively. The intricate network of rivers and streams in Utah, many originating in the high mountain ranges and carving their way through canyons, is intricately linked to the underlying topography. Understanding the elevation gradient is crucial for designing effective irrigation systems, managing water rights, and mitigating the impact of drought.
Infrastructure development, including road construction, pipeline routing, and building site selection, is also significantly influenced by elevation data. Determining the optimal routes for transportation networks requires careful consideration of elevation changes, slope gradients, and potential geological hazards. Similarly, selecting appropriate locations for buildings and infrastructure requires analyzing elevation to minimize risks associated with flooding, landslides, and seismic activity. The precise elevation data allows engineers and planners to make informed decisions that optimize safety, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact.
Furthermore, elevation data plays a vital role in ecological studies and environmental conservation. Mapping vegetation patterns and identifying critical habitats often relies on integrating elevation data with other geographical information such as soil type and climate data. This integrated approach enables researchers to understand the distribution of plant and animal species, identify areas of high biodiversity, and develop effective conservation strategies. The elevation gradient influences microclimates, creating distinct ecological zones, each supporting unique plant and animal communities.
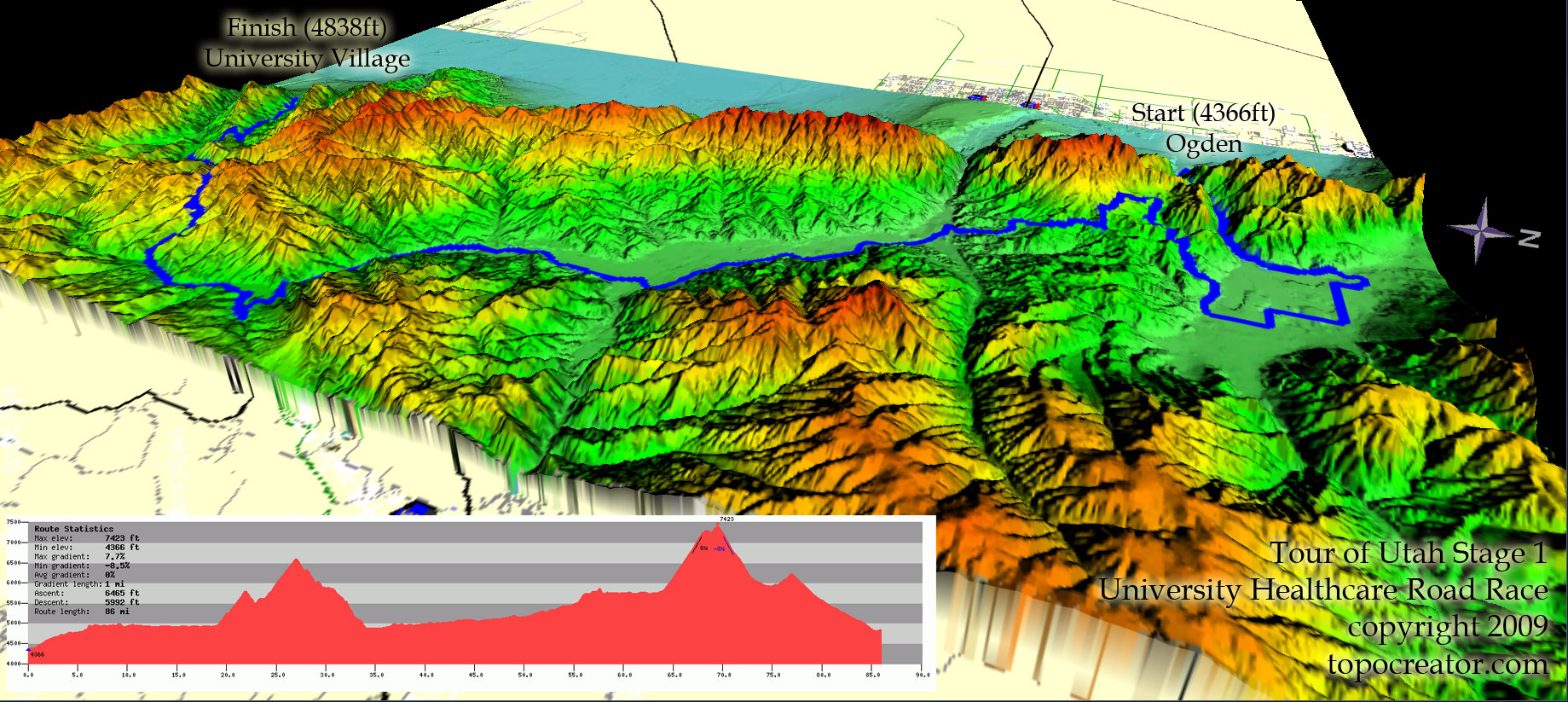
Recreational activities, from hiking and skiing to mountain biking and rock climbing, are heavily reliant on accurate elevation information. Topographic maps, derived from elevation data, provide essential information for navigating challenging terrains, planning routes, and assessing the difficulty of trails. Understanding elevation changes helps recreational users make informed decisions about safety and ensure a more enjoyable experience. The detailed elevation data allows for the creation of precise maps showcasing trail gradients, identifying potential hazards, and providing crucial information for emergency response.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
Q: What is the resolution of available Utah elevation data?
- A: The resolution varies depending on the data source. High-resolution data, suitable for detailed analysis and mapping, is available from sources like the USGS, but may be computationally intensive to process. Lower-resolution data is readily accessible for general use.
-
Q: Where can I access Utah elevation data?
- A: Several sources offer access to Utah elevation data, including the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the National Elevation Dataset (NED), and various state and local government agencies. These sources offer data in various formats, including raster and vector data.
-
Q: How is elevation data used in land management?
- A: Elevation data is essential for land management, informing decisions related to wildfire risk assessment, habitat restoration, grazing management, and sustainable forestry practices. It helps in identifying areas prone to erosion, landslides, and other natural hazards.
-
Q: What are the limitations of elevation data?
- A: Elevation data is a representation of the earth’s surface and is subject to limitations in accuracy and resolution. The data may not capture subtle changes in elevation or accurately reflect dynamic features like vegetation changes.
Tips for Utilizing Utah Elevation Data:
-
Data Selection: Carefully consider the resolution and accuracy required for the specific application. Higher-resolution data is more computationally demanding but provides greater detail.
-
Data Processing: Appropriate software and techniques are needed to process and analyze elevation data effectively. Familiarize yourself with GIS software and relevant data formats.
-
Data Integration: Combine elevation data with other geographical data layers, such as soil type, land cover, and climate data, for a more comprehensive analysis.
-
Visualization: Effective visualization of elevation data is crucial for interpretation and communication. Utilize appropriate mapping techniques to clearly represent the topographic features.
Conclusion:
The detailed elevation data available for Utah provides a powerful tool for understanding and managing the state’s complex and diverse environment. From informing crucial infrastructure decisions and guiding ecological research to supporting recreational activities and mitigating natural hazards, the applications are vast and multifaceted. The ongoing advancements in data acquisition and processing techniques continue to enhance the accuracy and accessibility of this critical geographical information, ensuring its continued importance in shaping the future of Utah’s development and conservation efforts. Effective utilization of this data requires a careful consideration of data sources, processing techniques, and visualization strategies to ensure accurate interpretation and informed decision-making.
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding Utah’s Topography: An Analysis of Elevation Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!