Illuminating the World: A Comprehensive Look at Night-Day Maps
Related Articles: Illuminating the World: A Comprehensive Look at Night-Day Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Illuminating the World: A Comprehensive Look at Night-Day Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Illuminating the World: A Comprehensive Look at Night-Day Maps

The Earth, a dynamic sphere constantly rotating on its axis, experiences a perpetual dance between light and darkness. This cyclical phenomenon, driven by the sun’s position relative to our planet, is visually captured in a fascinating cartographic representation known as a night-day map. These maps, often referred to as "day and night maps," serve as powerful tools for understanding global time zones, visualizing the distribution of sunlight, and analyzing various aspects of human activity and natural phenomena.
The Essence of a Night-Day Map
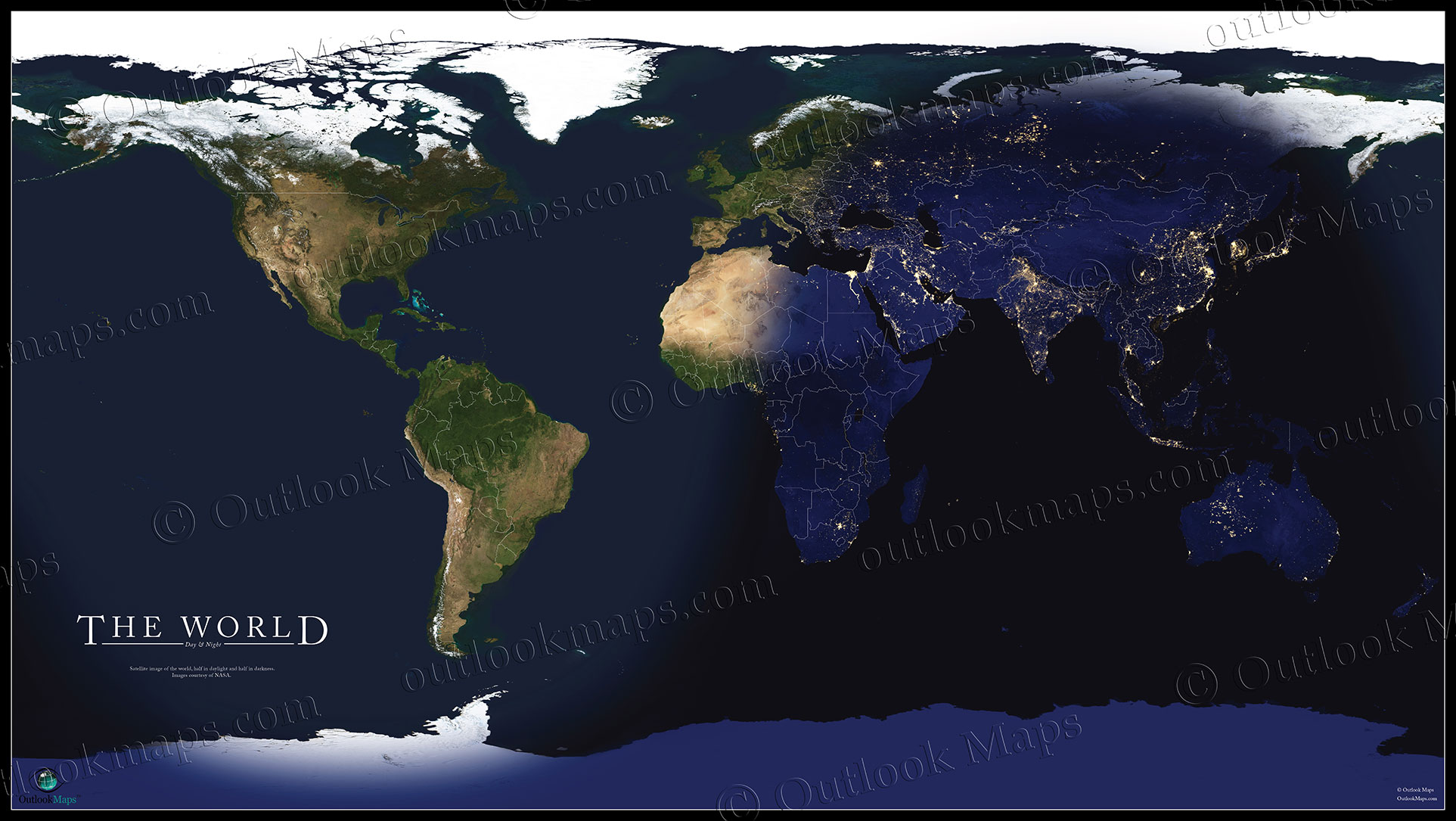
At its core, a night-day map depicts the Earth’s surface, highlighting the regions bathed in sunlight (daytime) and those shrouded in darkness (nighttime) at a specific point in time. This representation is achieved through a combination of color schemes, typically using bright shades for day and dark hues for night. The dividing line between these two zones, known as the terminator, is a dynamic curve that constantly shifts as the Earth rotates.
Beyond Visual Representation: The Significance of Night-Day Maps
While visually appealing, night-day maps hold far greater significance than mere aesthetics. Their utility extends across diverse fields, playing a crucial role in:
- Global Time Zones: By depicting the terminator’s movement, night-day maps offer a clear understanding of the progression of time across different longitudes. This information is vital for coordinating international communication, scheduling global events, and managing time-sensitive operations.
- Satellite Tracking and Communication: The terminator’s position directly impacts the availability of satellite communication and data transmission. Night-day maps allow for the optimization of satellite orbits and the efficient scheduling of data collection activities, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity and data flow.
- Weather Forecasting and Climate Analysis: The distribution of sunlight and darkness significantly influences weather patterns and climate dynamics. Night-day maps provide valuable insights into solar radiation levels, cloud formation, and temperature variations, assisting meteorologists in predicting weather events and understanding long-term climate trends.
- Environmental Monitoring and Disaster Response: Night-day maps aid in the monitoring of natural disasters, particularly those triggered by solar activity or extreme weather conditions. The visualization of the terminator’s position helps assess the potential impact of these events and enables prompt response efforts.
- Urban Planning and Development: The distribution of sunlight and darkness affects urban planning and development. Night-day maps assist in optimizing urban design for efficient energy use, minimizing light pollution, and creating more livable and sustainable urban environments.
- Astronomy and Space Exploration: Night-day maps are essential tools for astronomers and space explorers. They provide valuable information about the Earth’s position relative to the sun, aiding in the planning of space missions, observing celestial bodies, and understanding the Earth’s place in the solar system.
Dissecting the Components of a Night-Day Map
To fully grasp the insights gleaned from night-day maps, it’s crucial to understand their constituent elements:
- Terminator: This dynamic curve represents the boundary between day and night. It constantly shifts due to the Earth’s rotation, moving eastward at a rate of approximately 15 degrees per hour. The terminator’s position at any given moment determines the time zone and the amount of sunlight reaching different regions.
- Time Zones: Night-day maps often incorporate time zones, visually demonstrating how time varies across different longitudes. This information is crucial for understanding the global time system and coordinating international activities.
- Solar Radiation: Some night-day maps depict the intensity of solar radiation reaching different parts of the Earth. This data is valuable for understanding solar energy potential, climate change impacts, and weather forecasting.
- Cloud Cover: The presence of clouds can significantly impact the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface. Night-day maps can incorporate cloud cover information to provide a more accurate depiction of the distribution of light and darkness.
- Land and Water Features: The inclusion of land and water features provides context and helps users understand the geographical distribution of day and night.
FAQs Regarding Night-Day Maps
1. What is the difference between a night-day map and a world map?
While both maps depict the Earth’s surface, a night-day map focuses on the distribution of sunlight and darkness at a specific time, whereas a world map presents geographical features and political boundaries.
2. How often are night-day maps updated?
Night-day maps are typically updated in real-time, reflecting the constant movement of the terminator due to the Earth’s rotation.
3. Are night-day maps used for navigation?
While not directly used for navigation, night-day maps can provide valuable information about the time of day and the amount of sunlight in different locations, which can be helpful for planning trips or activities.
4. Can night-day maps be used to predict weather?
While not directly predicting weather, night-day maps can provide insights into solar radiation levels and cloud cover, which are crucial factors in weather forecasting.
5. How do night-day maps contribute to space exploration?
Night-day maps are essential for planning space missions, ensuring optimal satellite orbits, and understanding the Earth’s position relative to the sun.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing Night-Day Maps
- Pay attention to the time displayed on the map: This will determine the terminator’s position and the distribution of day and night.
- Analyze the terminator’s movement: Observe how the terminator shifts eastward as the Earth rotates, influencing time zones and sunlight distribution.
- Consider the impact of cloud cover: Clouds can significantly impact the amount of sunlight reaching the Earth’s surface, affecting the overall distribution of day and night.
- Utilize the map for time zone awareness: Night-day maps can be helpful for understanding global time zones and coordinating international activities.
- Explore different types of night-day maps: Various online platforms and mapping tools offer interactive night-day maps, allowing for customization and exploration.
Conclusion
Night-day maps, with their visually engaging portrayal of the Earth’s dynamic light and darkness, serve as more than mere cartographic representations. They offer a window into global time zones, satellite communication dynamics, weather patterns, and numerous other aspects of our planet. By understanding the principles behind these maps and their diverse applications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay of light and darkness that shapes our world. As technology continues to advance, night-day maps will undoubtedly play an even greater role in shaping our understanding of the Earth and its intricate workings.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Illuminating the World: A Comprehensive Look at Night-Day Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!