Mapping Haiti’s Seismic Scars: Understanding the Earthquake Risk and Its Impact
Related Articles: Mapping Haiti’s Seismic Scars: Understanding the Earthquake Risk and Its Impact
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Haiti’s Seismic Scars: Understanding the Earthquake Risk and Its Impact. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Haiti’s Seismic Scars: Understanding the Earthquake Risk and Its Impact

Haiti, a Caribbean nation steeped in history and resilience, has a tragic relationship with earthquakes. Its location on the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone, a major tectonic boundary, makes it highly vulnerable to seismic activity. Understanding the earthquake risk in Haiti necessitates a comprehensive view of the region’s geological landscape, which is vividly portrayed by earthquake maps.
The Enriquillo-Plantain Garden Fault Zone: A Seismic Hotspot
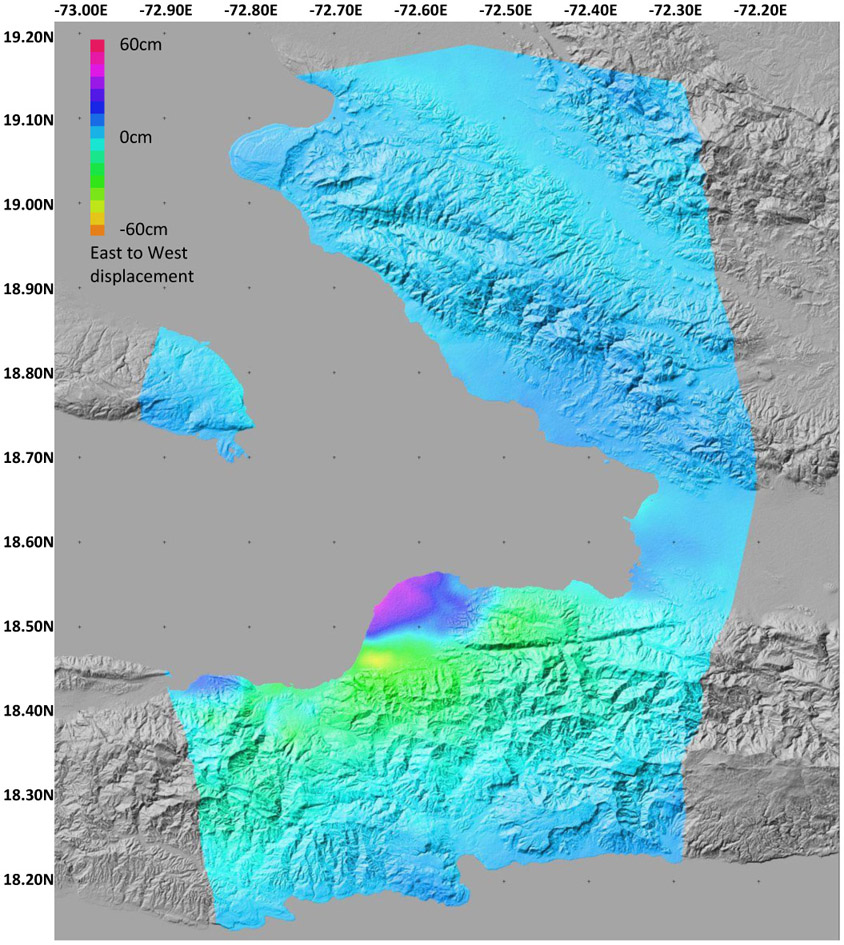
The Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone, a 600-kilometer-long transform fault, runs along the southern peninsula of Hispaniola, the island shared by Haiti and the Dominican Republic. This fault zone is where the Caribbean Plate and the North American Plate grind past each other, generating significant seismic energy. This constant movement creates a dynamic environment, with the potential for powerful earthquakes.
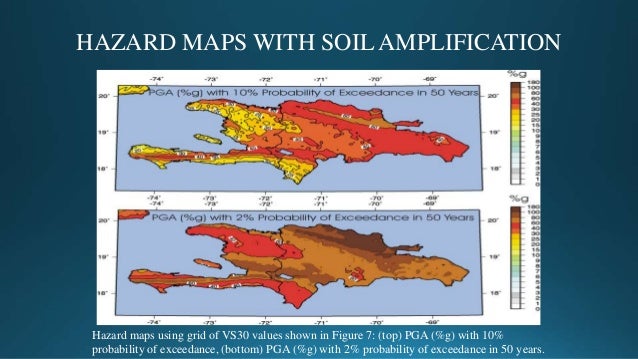
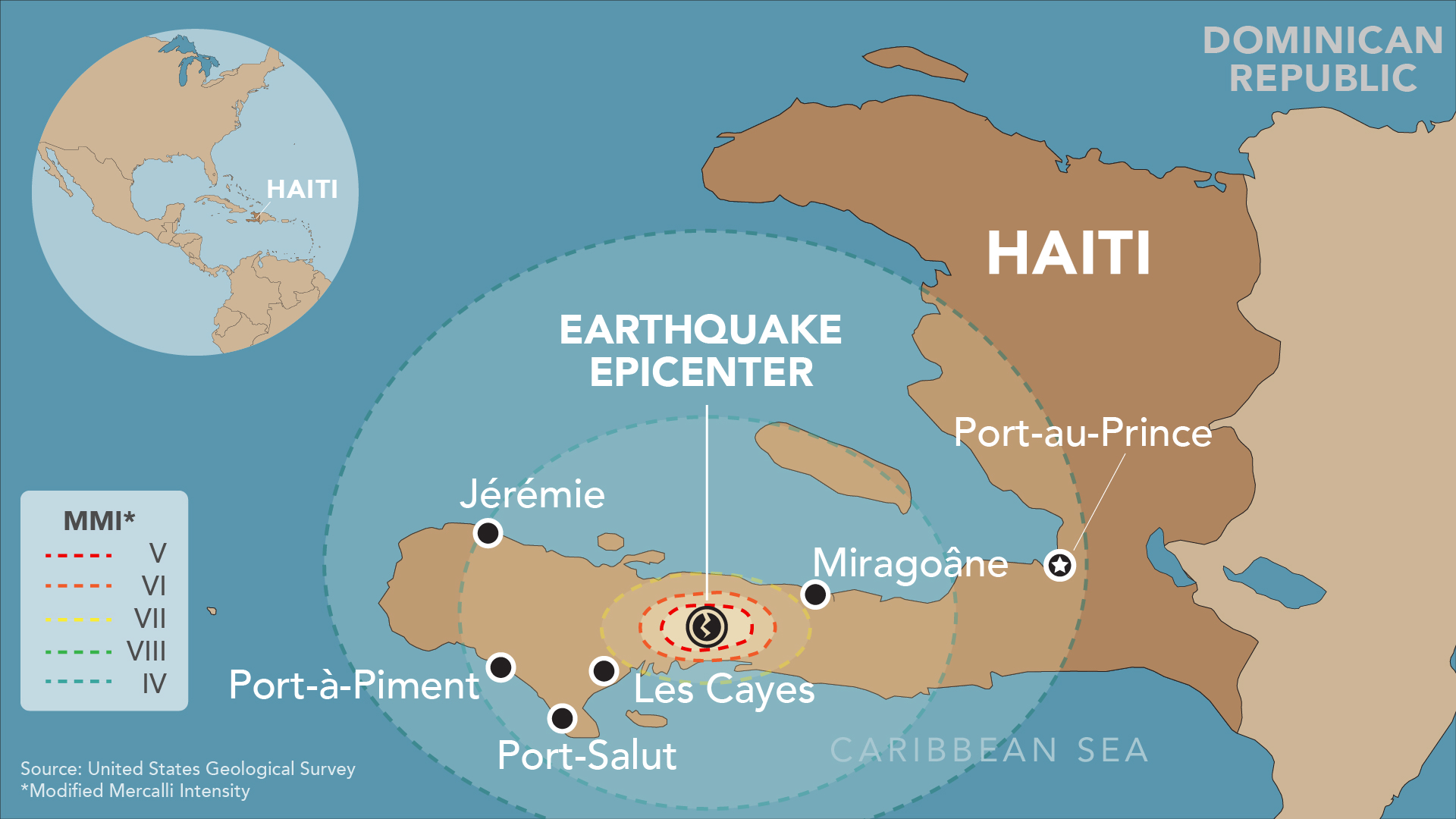
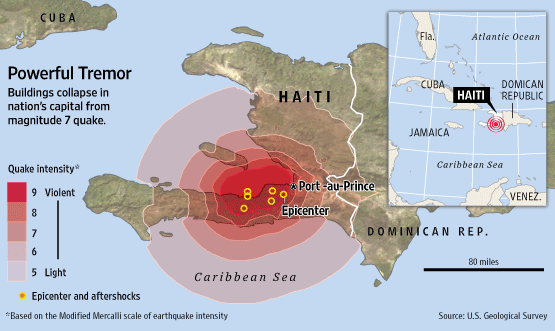
Haiti Earthquake Maps: A Visual Representation of Seismic Risk
Haiti earthquake maps are essential tools for understanding the country’s seismic vulnerability. These maps visualize various aspects of earthquake risk, including:
- Epicenter Locations: They pinpoint the exact locations where past earthquakes originated, providing valuable data for predicting future seismic activity.
- Magnitude and Intensity: Maps depict the magnitude and intensity of past earthquakes, indicating the potential for future earthquakes of similar strength.
- Fault Lines: They highlight the major fault lines, including the Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault zone, that are responsible for seismic activity.
- Seismic Hazard Zones: Maps delineate areas that are most susceptible to earthquakes, allowing for better risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
The Devastating Impact of the 2010 Earthquake
The 2010 Haiti earthquake, a magnitude 7.0 event, serves as a stark reminder of the catastrophic consequences of seismic activity. The earthquake’s epicenter was located near the city of Léogâne, approximately 25 kilometers west of Port-au-Prince, the capital. The earthquake triggered widespread destruction, causing significant damage to infrastructure, buildings, and homes.
The Importance of Haiti Earthquake Maps
Haiti earthquake maps are indispensable for:
- Risk Assessment: By identifying areas prone to earthquakes, these maps help authorities and communities understand the potential risks and prioritize mitigation efforts.
- Disaster Preparedness: Maps guide the development of emergency plans and evacuation routes, ensuring the safety of residents in the event of a seismic event.
- Infrastructure Design: They inform the design of buildings and infrastructure, incorporating seismic-resistant features to minimize damage during earthquakes.
- Land-Use Planning: Maps influence land-use planning decisions, minimizing development in high-risk areas and promoting sustainable development.
FAQs About Haiti Earthquake Maps
Q: What is the difference between magnitude and intensity?
A: Magnitude refers to the amount of energy released during an earthquake, measured on the Richter scale. Intensity, on the other hand, describes the earthquake’s effects on people, structures, and the environment.
Q: How often do earthquakes occur in Haiti?
A: Haiti experiences frequent earthquakes, with smaller tremors occurring regularly. Major earthquakes, like the 2010 event, are less frequent but still pose a significant threat.
Q: How accurate are Haiti earthquake maps?
A: Earthquake maps are constantly being updated with new data and improved scientific models. While they provide a valuable tool for understanding seismic risk, they cannot predict earthquakes with absolute certainty.
Q: What are some ways to prepare for an earthquake in Haiti?
A: Prepare a family emergency plan, including evacuation routes and meeting points. Secure heavy furniture and objects that could fall during an earthquake. Store essential supplies like food, water, and first aid kits.
Tips for Using Haiti Earthquake Maps
- Consult reliable sources: Refer to maps created by reputable organizations like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the Haitian government.
- Understand the map’s legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used to represent different aspects of earthquake risk.
- Consider your location: Identify your location on the map and assess the potential earthquake risks in your area.
- Share the information: Educate your family, friends, and community about the importance of earthquake preparedness.
Conclusion
Haiti earthquake maps serve as a critical tool for understanding the seismic vulnerability of the country. By visualizing the location and intensity of past earthquakes, fault lines, and seismic hazard zones, these maps provide valuable insights for risk assessment, disaster preparedness, infrastructure design, and land-use planning. While earthquakes cannot be predicted with absolute certainty, these maps empower communities to make informed decisions and build resilience against future seismic events. By understanding the risks and taking proactive measures, Haiti can mitigate the devastating impacts of earthquakes and work towards a safer future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Haiti’s Seismic Scars: Understanding the Earthquake Risk and Its Impact. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!