Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Related Articles: Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape
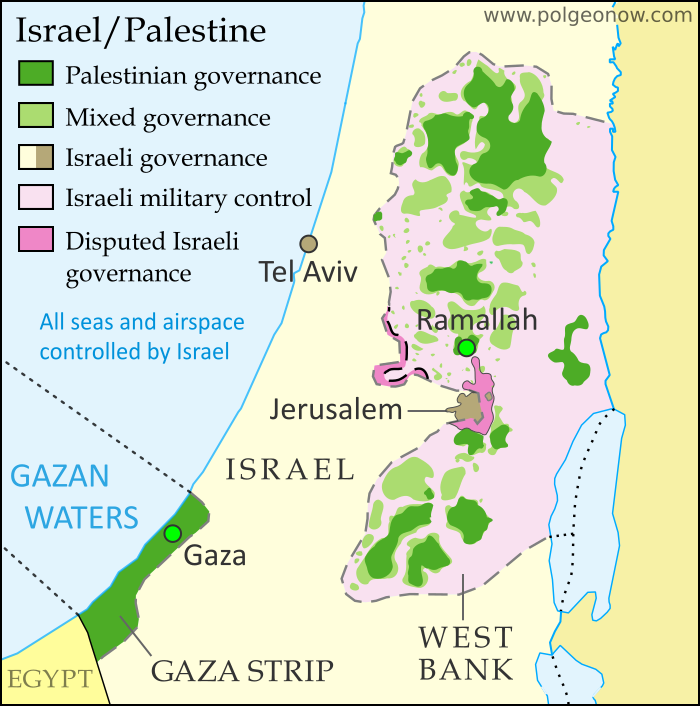
The Palestinian territories, encompassing the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip, represent a complex and contested landscape with a long and turbulent history. Understanding the geography of these territories is crucial for comprehending the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict and the challenges to achieving a lasting peace.
Defining the Territories:
The Palestinian territories are not a single contiguous entity, but rather three distinct regions separated by Israeli territory:
- The West Bank: Located west of the Jordan River, the West Bank is a hilly region with fertile valleys and a diverse population. It is divided into Area A, under full Palestinian control, Area B, under shared Israeli-Palestinian control, and Area C, under full Israeli control.
- East Jerusalem: This section of Jerusalem is claimed by both Palestinians and Israelis, with the latter controlling it since 1967. It is home to significant religious sites for both Muslims and Jews, including the Temple Mount/Haram al-Sharif.
- The Gaza Strip: A narrow coastal strip bordering Israel and Egypt, Gaza is densely populated and has been under an Israeli blockade since 2007. The Hamas militant group controls the territory.
Historical Context:
The current map of the Palestinian territories is the result of historical events and political decisions:
- The British Mandate: After World War I, the British administered Palestine, a territory encompassing the current Israeli and Palestinian territories. The mandate included a promise to establish a Jewish national home, but also a commitment to the rights of existing Arab inhabitants.
- The 1947 Partition Plan: The United Nations proposed a plan to divide Palestine into two states, one Jewish and one Arab. The plan was accepted by the Jewish leadership but rejected by the Arab leadership, leading to the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
- The 1967 Six-Day War: Israel captured the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip from Jordan and Egypt.
- The Oslo Accords: In the 1990s, a series of agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) aimed to create a Palestinian state in the West Bank and Gaza. However, these agreements were never fully implemented.
The Current Situation:
The current map of the Palestinian territories reflects the ongoing conflict, with Israeli settlements expanding in the West Bank and the Gaza Strip facing a severe humanitarian crisis. The status of East Jerusalem remains highly contentious, with both Israelis and Palestinians claiming it as their capital.
Significance of the Map:
The map of the Palestinian territories is crucial for understanding the following:
- The territorial claims of both Israelis and Palestinians: The map highlights the overlapping claims and the challenges of reaching a mutually acceptable solution.
- The impact of settlements on the Palestinian population: The map shows the physical separation between Israeli settlements and Palestinian communities, illustrating the difficulties faced by Palestinians in accessing resources and moving freely.
- The humanitarian situation in the Gaza Strip: The map depicts the isolation and vulnerability of the Gaza Strip, which is under Israeli blockade and suffers from severe economic and social challenges.
- The potential for a two-state solution: The map serves as a visual representation of the possible borders of a future Palestinian state, highlighting the need for land swaps and negotiations.
FAQs about the Map of the Palestinian Territories:
- What is the difference between the West Bank and Gaza Strip? The West Bank is located west of the Jordan River and is primarily controlled by Israel, while the Gaza Strip is a coastal territory controlled by Hamas and under Israeli blockade.
- What are the main Israeli settlements in the West Bank? Some of the main Israeli settlements in the West Bank include Ma’ale Adumim, Ariel, and Beit El.
- What is the status of East Jerusalem? East Jerusalem is claimed by both Israelis and Palestinians, but it is currently under Israeli control.
- What is the impact of the Israeli settlements on the Palestinian population? The settlements limit Palestinian movement, access to resources, and economic opportunities.
- What are the main challenges facing the Palestinian territories? Challenges include poverty, unemployment, lack of infrastructure, and the ongoing Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Tips for Understanding the Map of the Palestinian Territories:
- Consult multiple sources: Explore maps from different organizations and perspectives to get a comprehensive understanding.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the events and decisions that have shaped the current map.
- Focus on the human impact: Consider the impact of the map on the lives of Palestinians and Israelis.
- Engage with different perspectives: Explore the views of both Israelis and Palestinians on the map and its implications.
Conclusion:
The map of the Palestinian territories is a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. It highlights the territorial claims, the impact of settlements, and the challenges facing both Israelis and Palestinians. By understanding the geography of this contested landscape, we can gain a deeper understanding of the conflict and its potential for resolution. It is crucial to acknowledge the suffering and hardship experienced by both Israelis and Palestinians, and to advocate for a peaceful and just solution that respects the rights and aspirations of all parties involved.

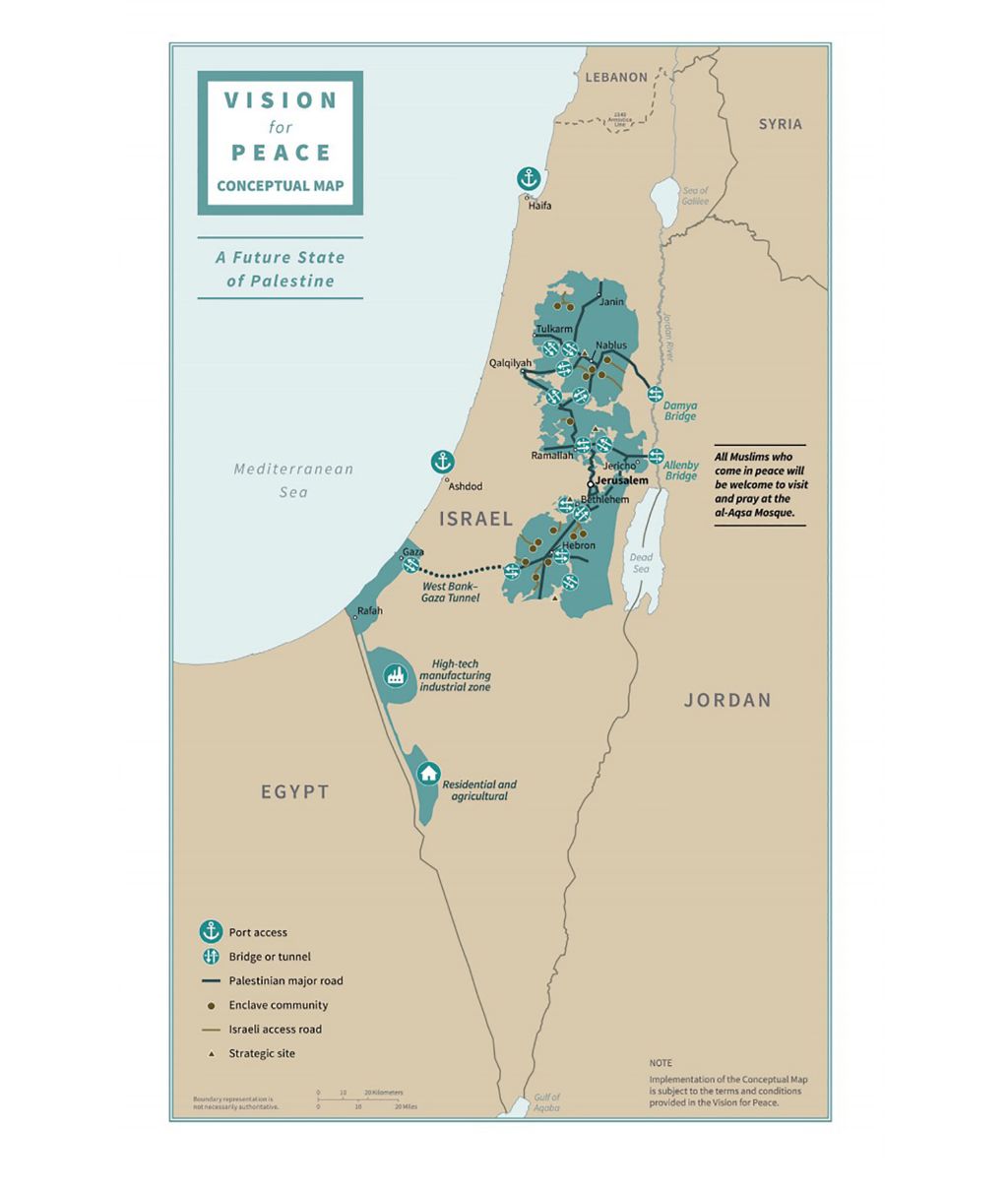

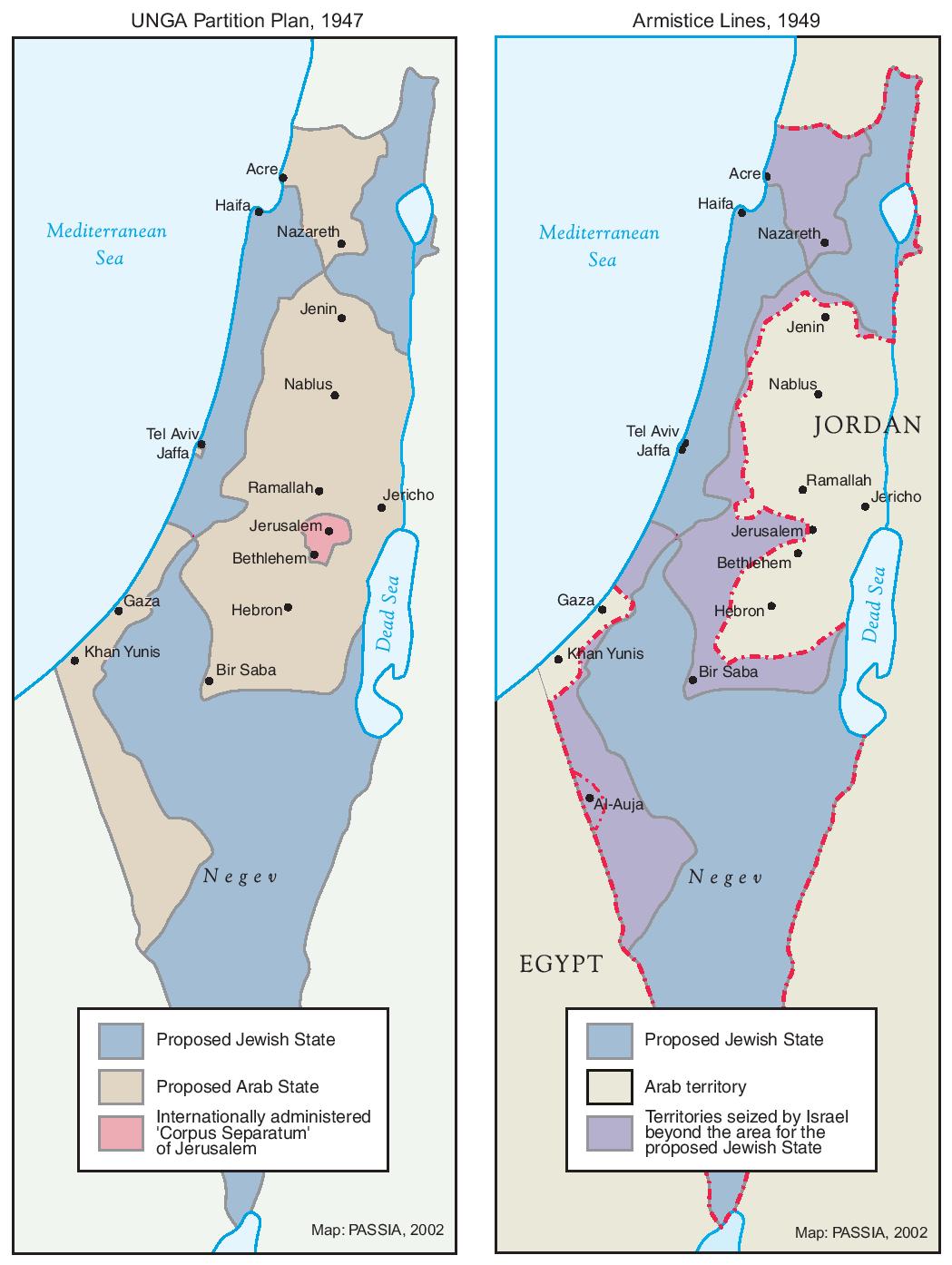
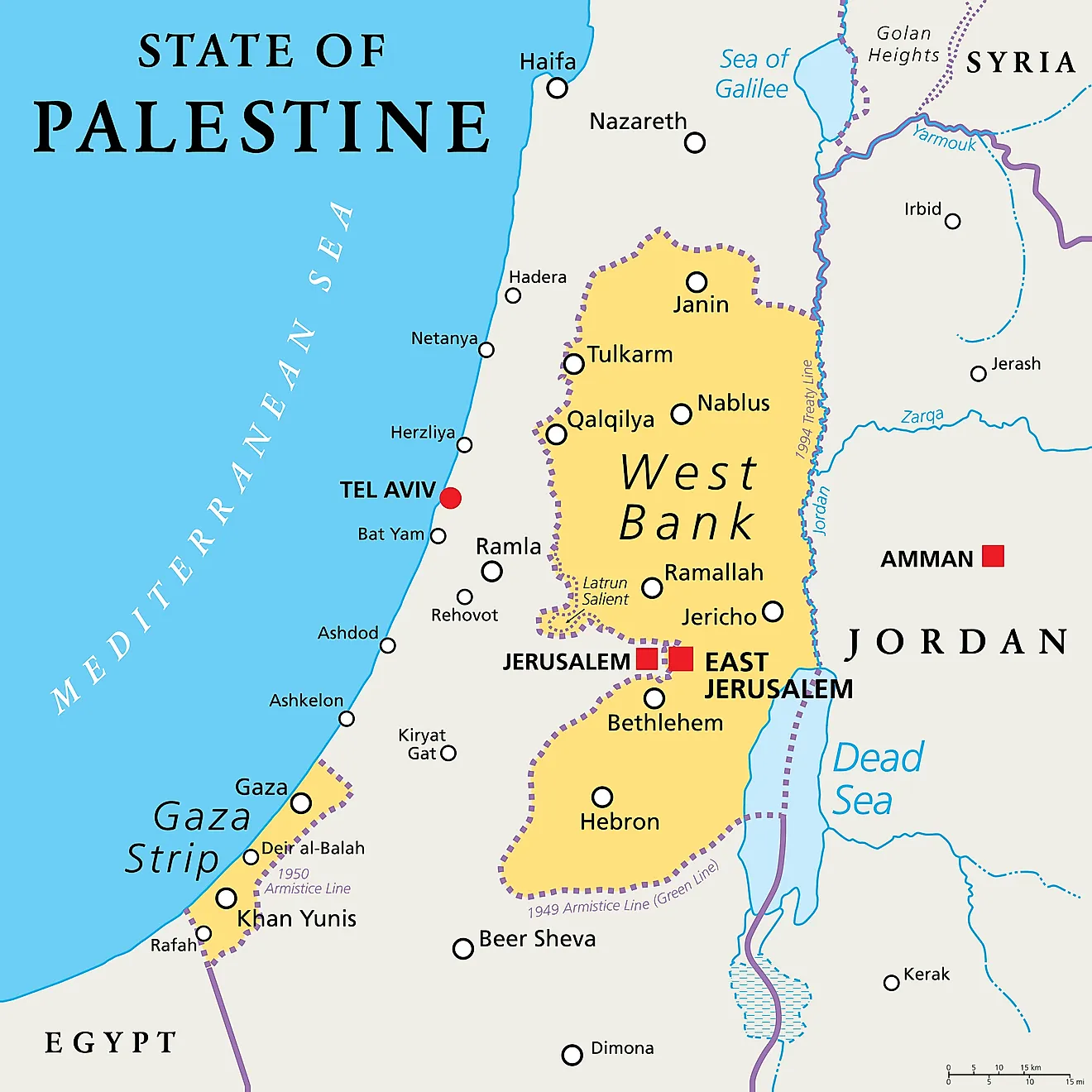
/cloudfront-ap-southeast-2.images.arcpublishing.com/nzme/OPROIYFQTOAN4FCQMY5YTOZRBY.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Palestinian Territories: A Complex and Contested Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!