Navigating Higher Education in the United States: A Geographic Perspective
Related Articles: Navigating Higher Education in the United States: A Geographic Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Higher Education in the United States: A Geographic Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Higher Education in the United States: A Geographic Perspective
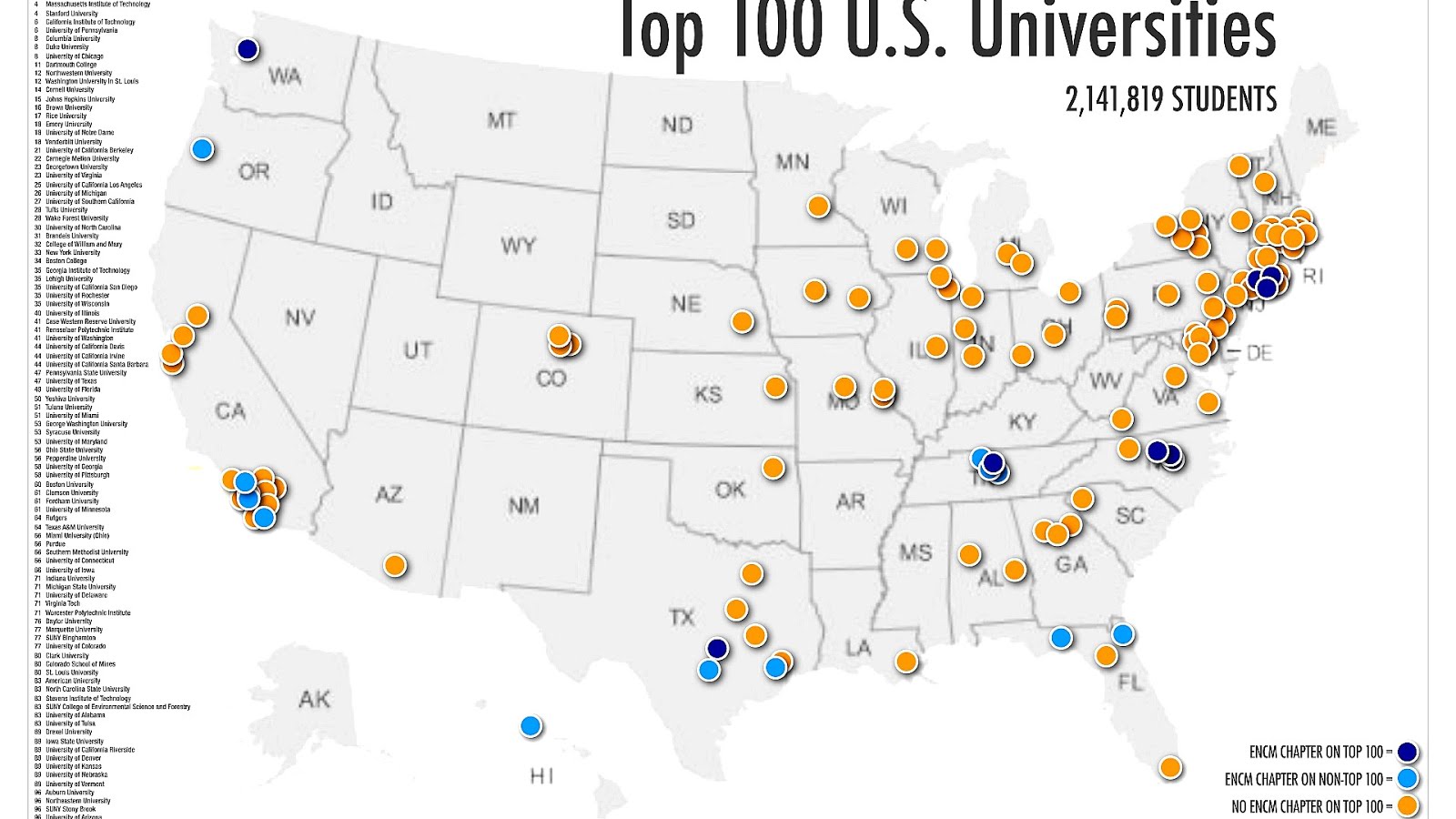
The United States boasts a vast and diverse higher education landscape, encompassing thousands of institutions ranging from small liberal arts colleges to sprawling research universities. Understanding the geographical distribution of these institutions provides crucial insights into access, specialization, and the overall structure of the American higher education system. Visual representations of this distribution, often in map format, are invaluable tools for prospective students, researchers, policymakers, and anyone interested in the higher education sector.
These cartographic representations typically depict institutions using different markers or color-coding to distinguish between public and private institutions, research intensity, size, or specific academic strengths. For example, a map might highlight the concentration of Ivy League universities in the Northeast, the prevalence of large public universities in the Midwest and South, or the growth of technology-focused institutions in California and the Pacific Northwest. Such visualizations quickly reveal geographical patterns and disparities in access to higher education. Rural areas, for instance, often exhibit lower density of institutions compared to urban centers, potentially impacting access for students in those regions.
Beyond simple location, these maps can incorporate additional layers of information. Data on tuition costs, graduation rates, student demographics, and research funding can be overlaid to provide a more nuanced understanding of institutional characteristics and their spatial distribution. This allows for analysis of regional variations in affordability, student success, and research output. For example, one might observe a correlation between high tuition costs and proximity to major metropolitan areas, or a concentration of research funding in specific regions known for their technological innovation.
The value of these visual tools extends beyond simple observation. They facilitate comparative analysis, enabling researchers to identify clusters of institutions with similar characteristics, or to pinpoint areas with a shortage of specific types of institutions. For instance, a map could reveal a lack of medical schools in a particular region, highlighting a potential need for investment in healthcare education. Similarly, analysis of the geographic distribution of specific programs, such as engineering or agricultural sciences, can inform strategic planning and resource allocation.
Policymakers utilize such data to understand the impact of educational policies on different regions. The influence of state funding models on the development of public institutions, for example, is readily apparent when analyzing the geographic distribution of these institutions and their relative resource levels. Similarly, the effectiveness of initiatives aimed at increasing access to higher education in underserved communities can be assessed through spatial analysis of enrollment patterns and institutional location.
Furthermore, these maps serve as valuable resources for prospective students. By visually exploring the geographic distribution of institutions and their associated characteristics, students can identify institutions that align with their academic goals, financial circumstances, and personal preferences. The ability to filter and sort institutions based on various criteria, such as location, size, and academic programs, greatly simplifies the college search process.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What types of data are typically included on these maps? Common data points include institution type (public/private), size (enrollment), academic focus (research, liberal arts, etc.), location, and sometimes additional metrics like tuition costs, graduation rates, and research funding.
-
How accurate are these maps? The accuracy depends on the data source and the methodology used to create the map. Data from reliable sources like the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) generally provides a high degree of accuracy.
-
Are there limitations to using these maps? Maps provide a visual summary of data, but they cannot capture the full complexity of each institution. Further research is always recommended before making decisions based solely on map data.
-
Where can these maps be found? Many organizations, including the NCES, individual universities, and various educational data providers, offer interactive maps of US universities.
-
How are these maps used in research? Researchers employ these maps for spatial analysis, identifying clusters, correlations, and disparities in access and resources within the higher education system.
Tips for Utilizing University Location Data
-
Consider multiple data sources: Utilize information from various sources to obtain a comprehensive understanding of institutional characteristics.
-
Focus on relevant criteria: Prioritize data points that align with individual needs and research objectives.
-
Interpret data cautiously: Recognize the limitations of visual representations and avoid overgeneralizations.
-
Combine map data with other information: Supplement map data with institutional websites, brochures, and other relevant materials.
-
Engage in critical analysis: Evaluate data critically, considering potential biases and limitations.
Conclusion
Visual representations of the US higher education landscape offer a powerful tool for understanding the geographic distribution of institutions and their associated characteristics. These maps facilitate comparative analysis, inform policy decisions, and assist prospective students in their college search. While these visual tools provide valuable insights, they should be used in conjunction with other data sources and a critical approach to ensure a complete and nuanced understanding of the complex and dynamic nature of the American higher education system. Further research and exploration of individual institutions remain crucial for making informed decisions.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Higher Education in the United States: A Geographic Perspective. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!