Navigating the Labyrinth: A Guide to Japan’s Train Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth: A Guide to Japan’s Train Network
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth: A Guide to Japan’s Train Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Labyrinth: A Guide to Japan’s Train Network

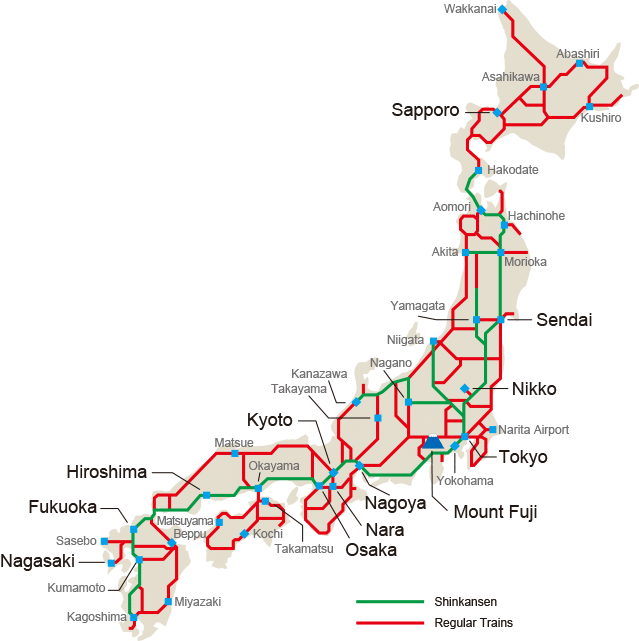
Japan’s intricate web of railway lines, a testament to the nation’s dedication to efficiency and precision, can seem daunting to the uninitiated. However, beneath the seemingly complex tapestry of lines and stations lies a remarkably well-organized system, offering unparalleled connectivity and convenience to travelers. This article aims to unravel the mysteries of the Japanese train map, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding its structure, navigating its intricacies, and maximizing its benefits.
A Tapestry of Lines and Operators:
The first step in understanding Japan’s train system is recognizing the diverse network of operators. While the term "Japan Rail" (JR) is often used to denote the national railway network, it actually encompasses multiple independent companies, each responsible for specific regions and lines. These include:
- JR East: Serving the eastern region, including Tokyo, Hokkaido, and the Tohoku region.
- JR Central: Operating lines in the central region, including Nagoya, Osaka, and the Chubu region.
- JR West: Responsible for the western region, encompassing Osaka, Kyoto, and the Kansai region.
- JR Shikoku: Covering the Shikoku Island.
- JR Kyushu: Operating lines in the Kyushu Island.
Beyond these major operators, numerous private railway companies also contribute to the extensive network. These companies often focus on specific regions or urban areas, providing services that complement the national network.
Decoding the Symbols:
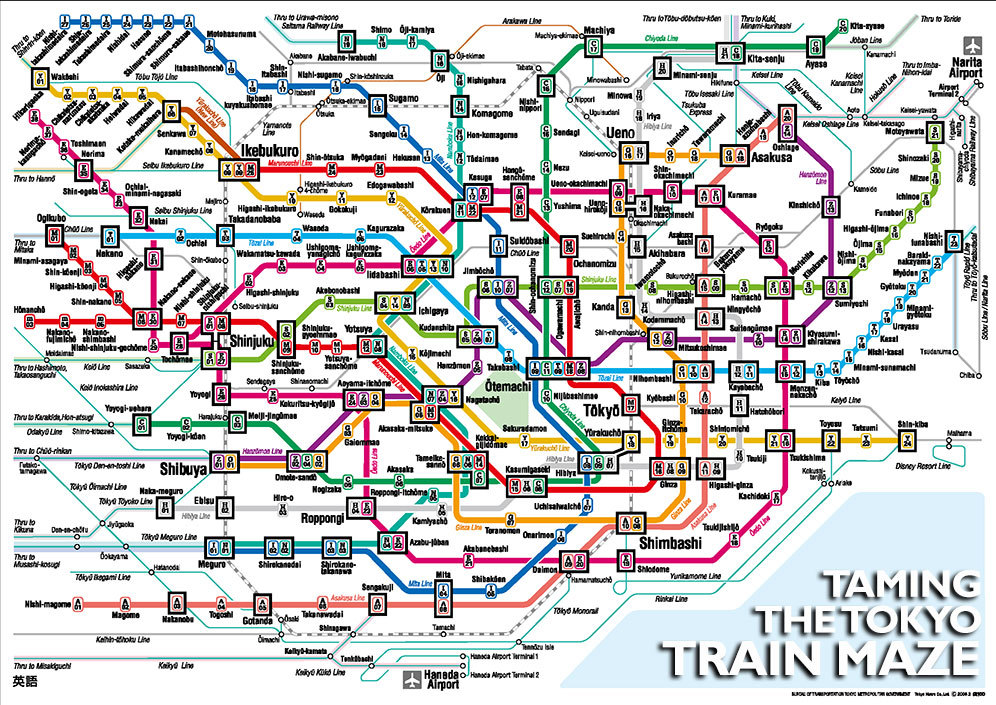
The Japanese train map, often displayed in stations and on train carriages, features a unique visual language that requires some decoding. Understanding these symbols is crucial for effectively navigating the system:
- Line Colors: Each line is assigned a distinct color, aiding in visual identification and route planning.
- Line Names: Lines are often labeled with unique names, like "Shinkansen," "Tohoku Line," or "Keihin-Tohoku Line."
- Station Icons: Stations are marked with distinct symbols, often representing their location or significance.
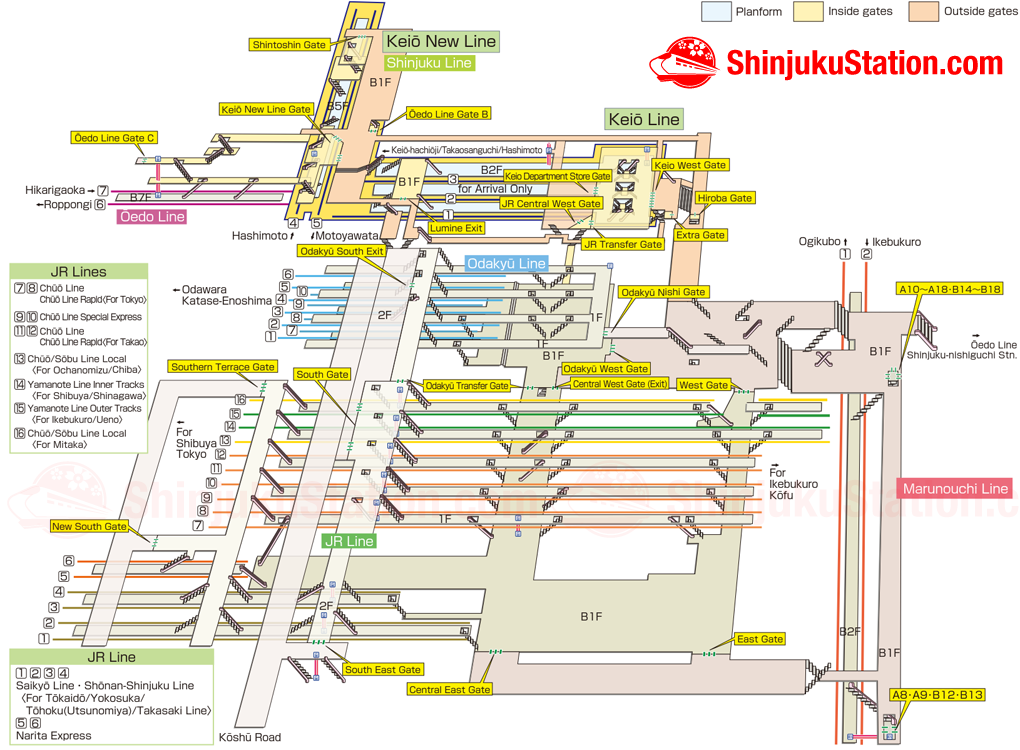
- Transfer Points: Major stations serving as transfer points between different lines are highlighted with larger icons.
The Importance of "Shinkansen":
The "Shinkansen," or "bullet train," stands as the crown jewel of Japan’s railway system. These high-speed trains traverse the country at remarkable speeds, connecting major cities with unparalleled efficiency. The Shinkansen network is further divided into different lines, each serving specific routes and destinations.
Navigating the System:
- Ticket Purchase: Tickets are typically purchased at automated ticket machines or manned counters at stations. Travelers need to specify their starting and ending stations, and the machine will calculate the fare.
- Boarding: Passengers board trains at the designated platform indicated on their tickets. The platform number is displayed on the station’s information boards.
- Announcements: Stations and trains feature audio and visual announcements in both Japanese and English, guiding passengers on platform changes, destination information, and other crucial details.
Benefits of Japan’s Train System:
- Efficiency: The well-organized system ensures punctuality and speed, minimizing travel time between destinations.
- Convenience: The extensive network provides access to virtually every corner of the country, eliminating the need for long-distance flights or road trips.
- Safety: Japan’s railway system boasts an impeccable safety record, with stringent regulations and advanced technology ensuring passenger security.
- Comfort: Trains offer comfortable seating arrangements, ample legroom, and often include amenities like Wi-Fi and power outlets.
- Sustainability: The reliance on rail transportation contributes to a reduced carbon footprint and promotes environmental sustainability.
FAQs:
- Q: How do I purchase tickets for the Shinkansen?
- A: Shinkansen tickets can be purchased at designated ticket machines or counters at stations. Travelers can choose from various ticket types, including reserved and non-reserved seats.
- Q: Are there English announcements on trains?
- A: Most Shinkansen and major train lines feature English announcements, along with Japanese, providing information on destinations, platform changes, and other essential details.
- Q: How do I navigate the different lines and transfer stations?
- A: The train map, displayed at stations and on train carriages, provides a visual guide to the network. Passengers can follow the color-coded lines and station icons to navigate their route.
- Q: What are the different types of train passes available?
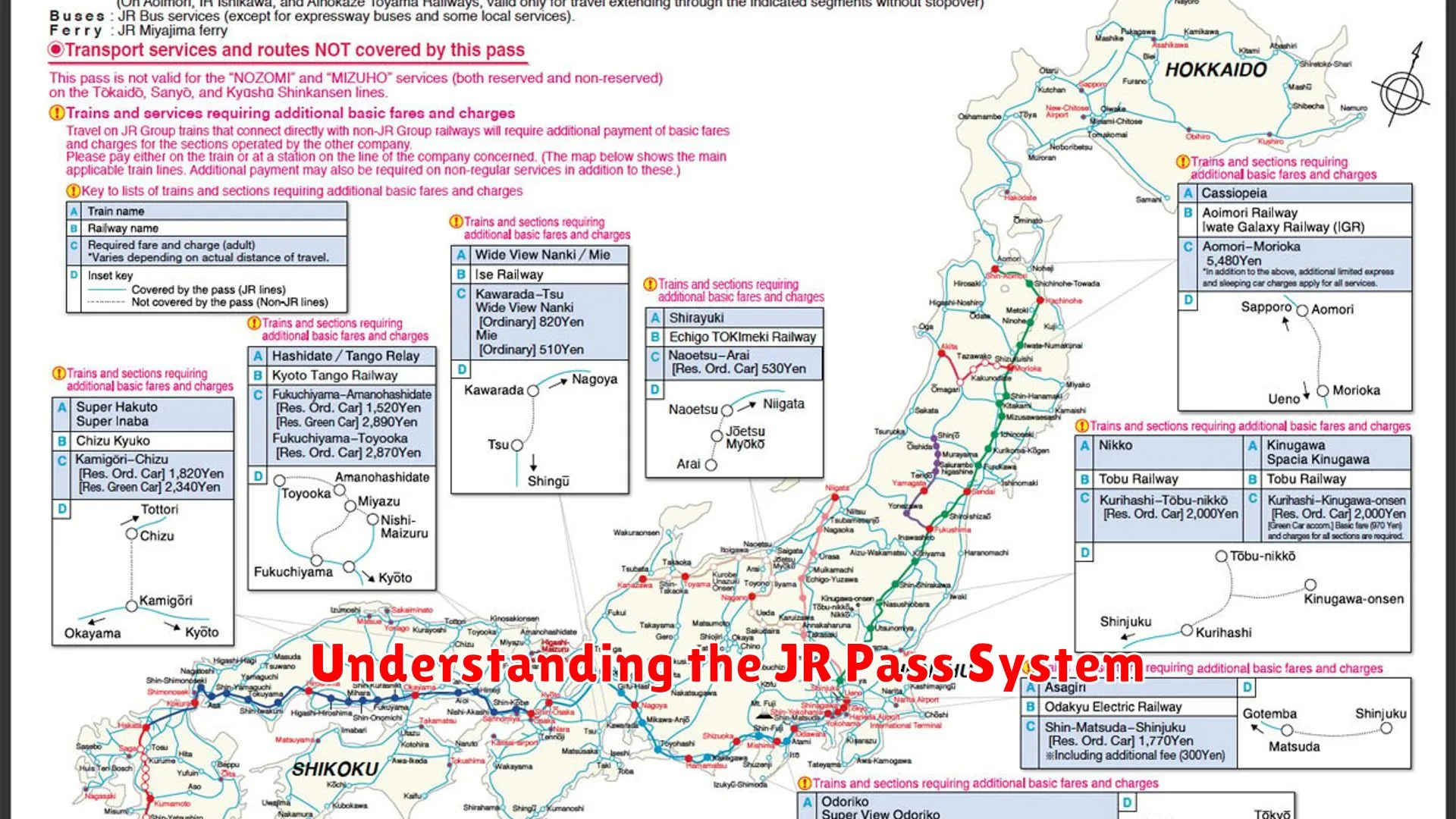
- A: Japan offers various train passes, including the Japan Rail Pass, which provides unlimited travel on JR lines for a set period. Other passes, like the Seishun 18 Kippu, offer discounted fares for younger travelers.
- Q: What are the main differences between the Shinkansen and regular trains?
- A: The Shinkansen, or "bullet train," operates at significantly higher speeds, connecting major cities with unparalleled efficiency. Regular trains offer a slower pace of travel, often serving smaller towns and local destinations.
Tips:
- Plan your route in advance: Utilize online resources and apps to map your journey and identify the most suitable lines and stations.
- Purchase tickets early: Ensure a smooth journey by purchasing tickets in advance, especially for popular routes or during peak travel seasons.
- Learn basic Japanese phrases: While English announcements are common, understanding basic Japanese phrases can enhance communication and navigation.
- Respect train etiquette: Maintain a quiet demeanor, avoid loud conversations, and refrain from eating or drinking on trains.
- Utilize station amenities: Take advantage of the facilities available at stations, including lockers, restrooms, and information desks.
Conclusion:
Japan’s train network stands as a testament to the nation’s commitment to efficiency, precision, and innovation. Navigating this intricate system may initially seem daunting, but with a little understanding and preparation, travelers can unlock its unparalleled benefits. From the high-speed thrill of the Shinkansen to the convenience of local lines, Japan’s train system offers a seamless and efficient mode of transportation, enriching the travel experience and providing access to the country’s hidden treasures.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth: A Guide to Japan’s Train Network. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!