Navigating the Landscape of Libya: A Geographic Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Libya: A Geographic Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Libya: A Geographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Libya: A Geographic Exploration
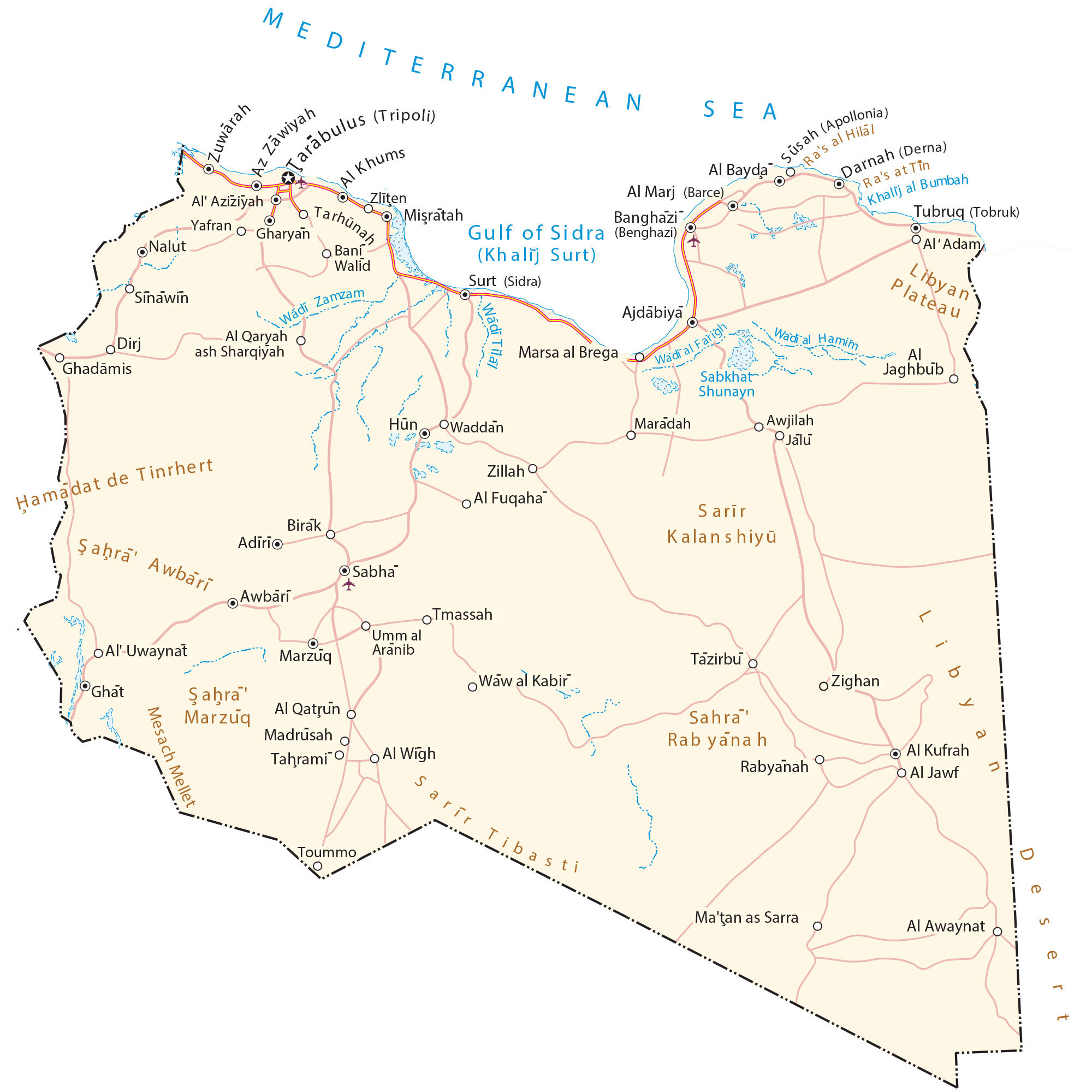
Libya, a North African nation nestled along the Mediterranean coast, occupies a strategic position on the world map. Its vast expanse, encompassing a diverse terrain of deserts, mountains, and coastal plains, has shaped its history, culture, and present-day challenges. Understanding the geography of Libya is essential for comprehending its complexities and appreciating its potential.
A Land of Extremes:
Libya’s geography is defined by extremes. It is the largest country in Africa by land area, with a coastline stretching over 1,770 kilometers. The vast majority of its territory is dominated by the Sahara Desert, covering approximately 90% of its landmass. This unforgiving landscape, characterized by vast sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and occasional oases, presents formidable challenges for human habitation and economic development.
However, the desert is not a uniform entity. The Libyan Sahara encompasses diverse landscapes, from the vast, rolling dunes of the Erg Awbari to the rocky highlands of the Tibesti Mountains. These mountains, reaching heights of over 3,000 meters, are home to unique biodiversity and hold significant water resources.
Coastal Contrasts:
In stark contrast to the harsh desert, Libya’s Mediterranean coastline offers a lifeline of fertile land and vital resources. The coastal strip, known as the "Jefara," is characterized by fertile plains and coastal oases, providing a haven for agriculture and urban development. Major cities like Tripoli, Benghazi, and Misrata flourish along this narrow strip, drawing economic activity and population density.
Strategic Location and Global Connections:
Libya’s strategic location at the crossroads of North Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Sahara Desert has historically made it a key player in regional and global affairs. Its proximity to Europe, the Middle East, and sub-Saharan Africa has made it a crucial route for trade, migration, and cultural exchange.
The country’s coastline offers access to important shipping lanes connecting Europe with Asia and Africa. This strategic position has also drawn attention from global powers throughout history, leading to periods of foreign influence and political instability.
Resource Riches and Economic Potential:
Libya is blessed with abundant natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. These resources have played a significant role in its economic development, but their uneven distribution and dependence on global markets have also contributed to economic volatility and social inequalities.
The country’s vast desert holds untapped potential for renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. These resources offer a path towards sustainable development and diversification of the Libyan economy, moving away from its reliance on fossil fuels.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its rich resources and strategic location, Libya faces numerous challenges. The country has experienced prolonged periods of political instability, conflict, and economic hardship, hindering its development and impacting its people’s lives.
The need for political reconciliation, infrastructure development, and sustainable economic diversification remains critical. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from the Libyan people, regional partners, and the international community.
Navigating the Future:
Libya’s geographic landscape presents both challenges and opportunities. Its vast desert and strategic location offer potential for sustainable development, while its rich natural resources hold the key to economic prosperity.
Overcoming the challenges of political instability and economic inequality will require collaborative efforts to harness the potential of Libya’s diverse geography and build a future of peace, prosperity, and sustainable development.
FAQs about Libya’s Geography:
Q: What is the highest point in Libya?
A: The highest point in Libya is the volcanic peak of Bikku Bitti in the Tibesti Mountains, reaching a height of 3,415 meters.
Q: What are the major rivers in Libya?
A: Libya has no permanent rivers due to its arid climate. However, there are numerous wadis, dry riverbeds that occasionally fill with water during periods of rainfall.
Q: What is the climate like in Libya?
A: Libya experiences a hot desert climate with very little rainfall. Temperatures can reach extreme highs in the summer, particularly in the interior desert regions.
Q: What are the major cities in Libya?
A: The major cities in Libya include Tripoli, Benghazi, Misrata, and Sebha. These cities are located along the Mediterranean coast or in areas with access to water resources.
Q: What is the population density of Libya?
A: Libya has a low population density due to its vast desert landscape. The majority of the population is concentrated along the Mediterranean coast and in a few oases.
Tips for Understanding Libya’s Geography:
- Use maps and satellite imagery: Visualizing Libya’s geography through maps and satellite imagery provides a clear understanding of its diverse landscapes and strategic location.
- Study the history of Libya: Understanding the historical context of Libya’s geography is essential for comprehending its present-day challenges and opportunities.
- Learn about the culture and traditions of Libya: The cultural landscape of Libya is closely intertwined with its geography. Learning about its diverse tribes, languages, and traditions provides a deeper understanding of the country.
- Explore the role of natural resources: Understanding the distribution and utilization of Libya’s natural resources, particularly oil, gas, and renewable energy, is crucial for comprehending its economic potential and challenges.
- Stay informed about current events: Staying informed about the political and economic situation in Libya helps to grasp the complexities of its geography and its impact on the lives of its people.
Conclusion:
Libya’s geography is a defining feature of its history, culture, and present-day challenges. Its vast desert, strategic location, and rich natural resources present both opportunities and obstacles for development. Understanding the nuances of its landscape is essential for navigating the complexities of this North African nation and appreciating its potential for a brighter future. By embracing collaboration, sustainable practices, and a commitment to peace and prosperity, Libya can harness the power of its geography to build a future worthy of its people and its unique landscape.
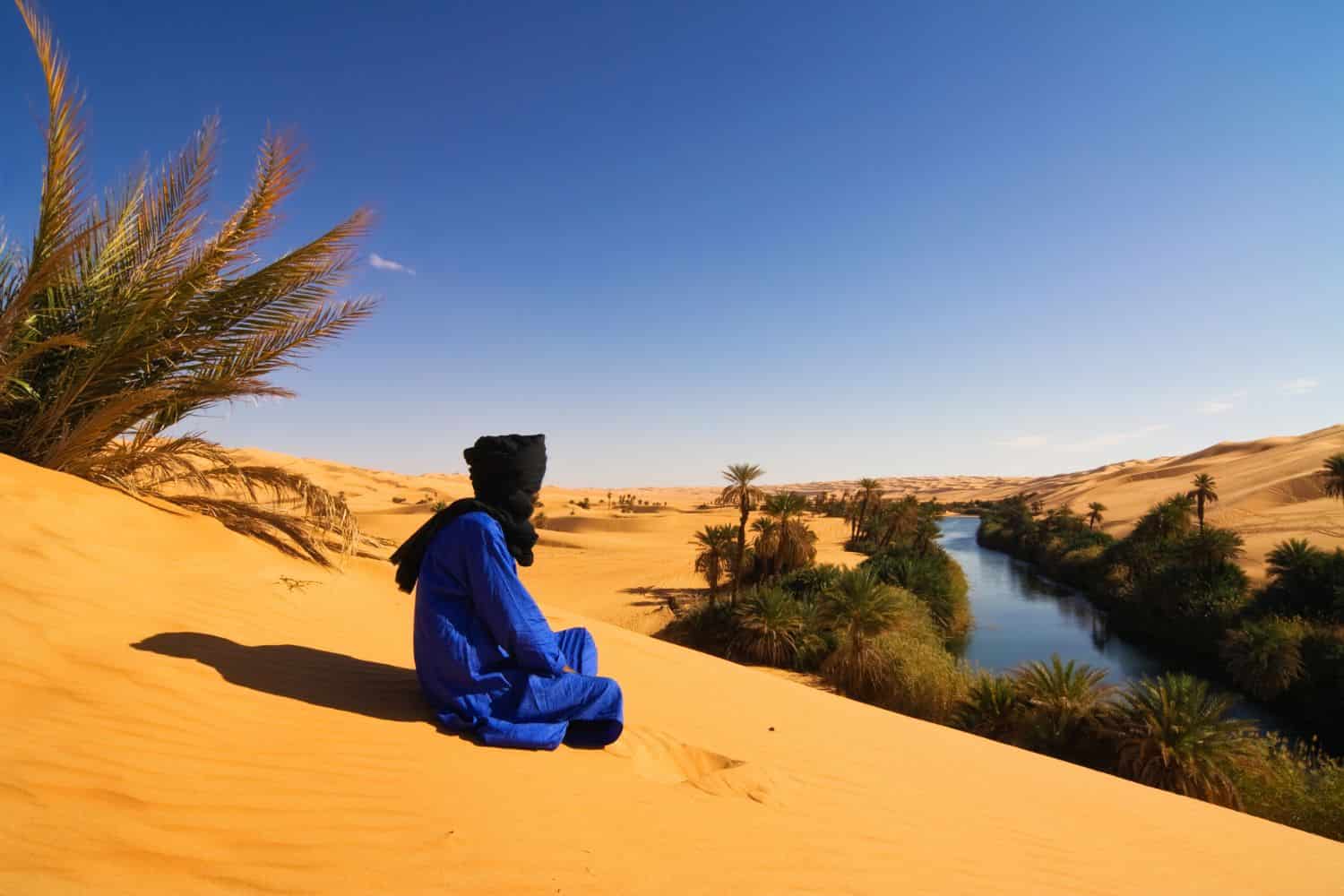
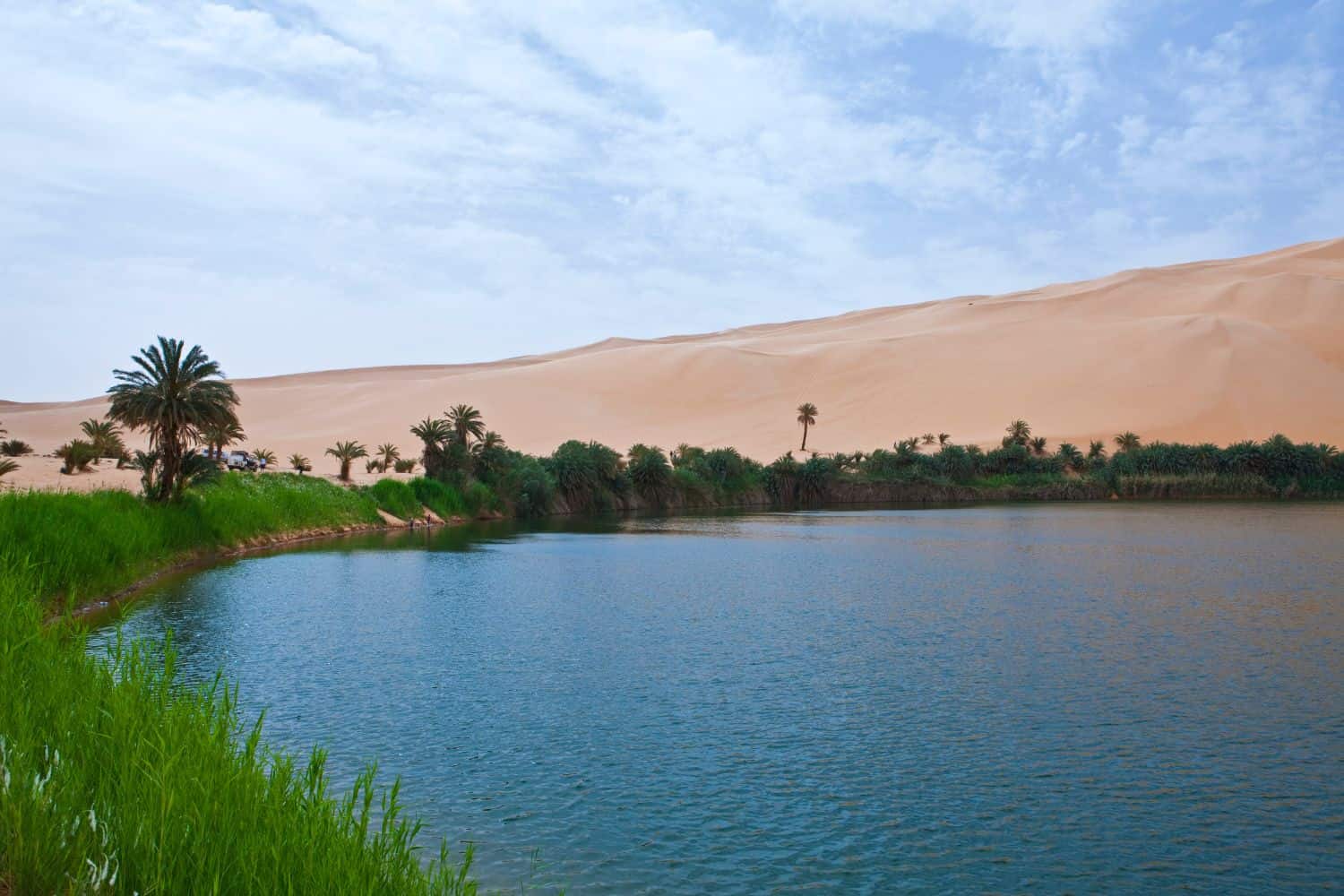

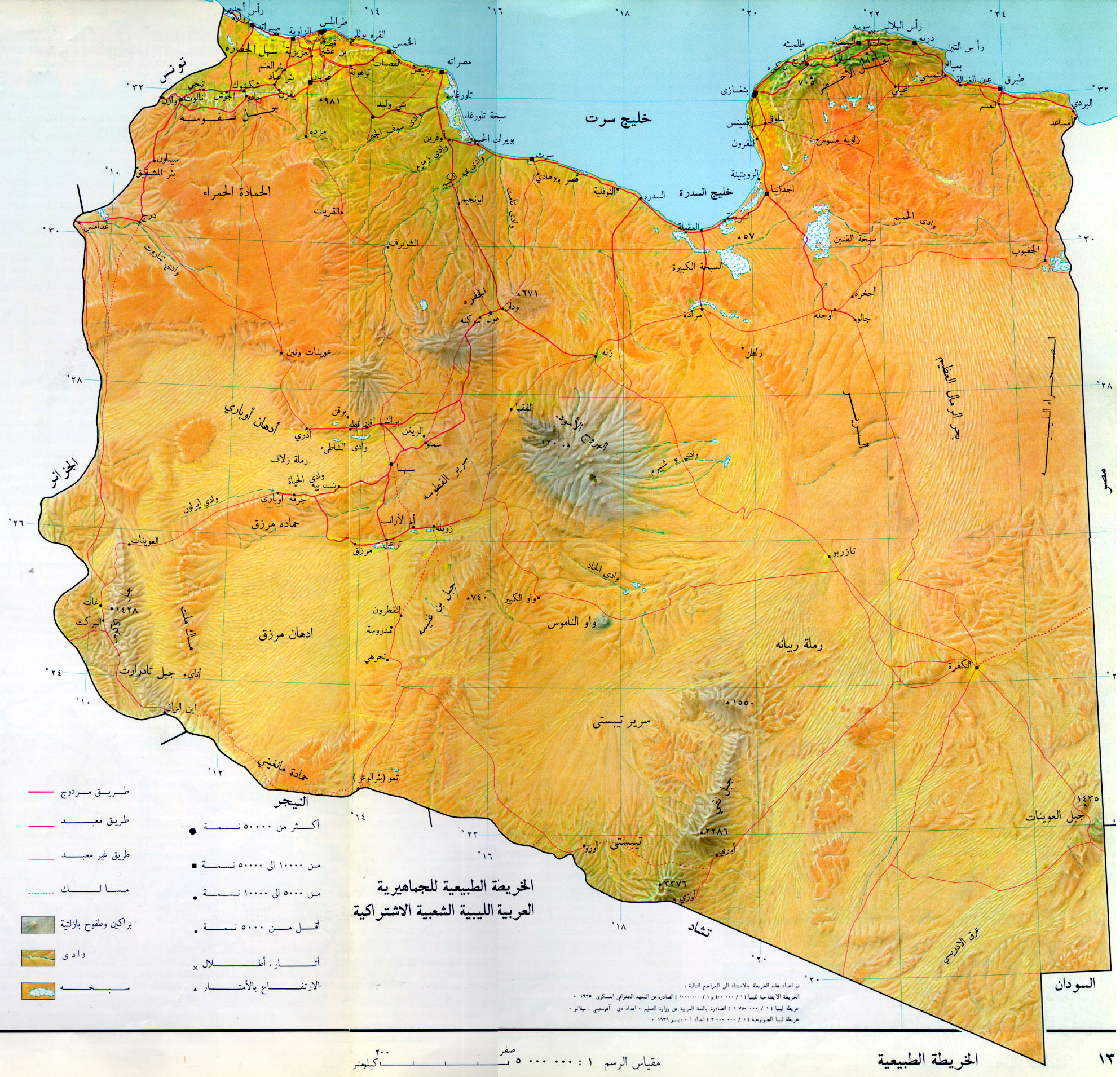




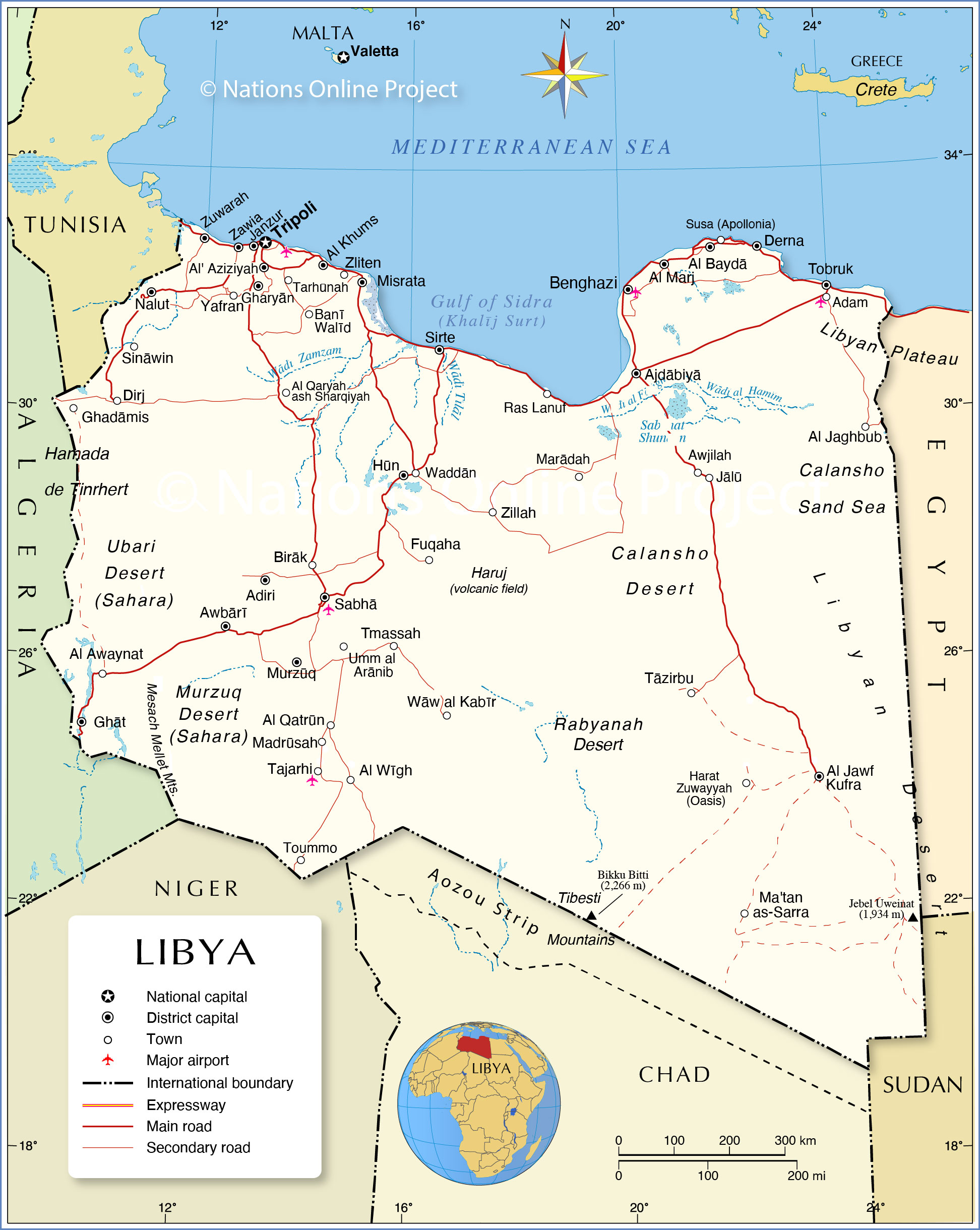
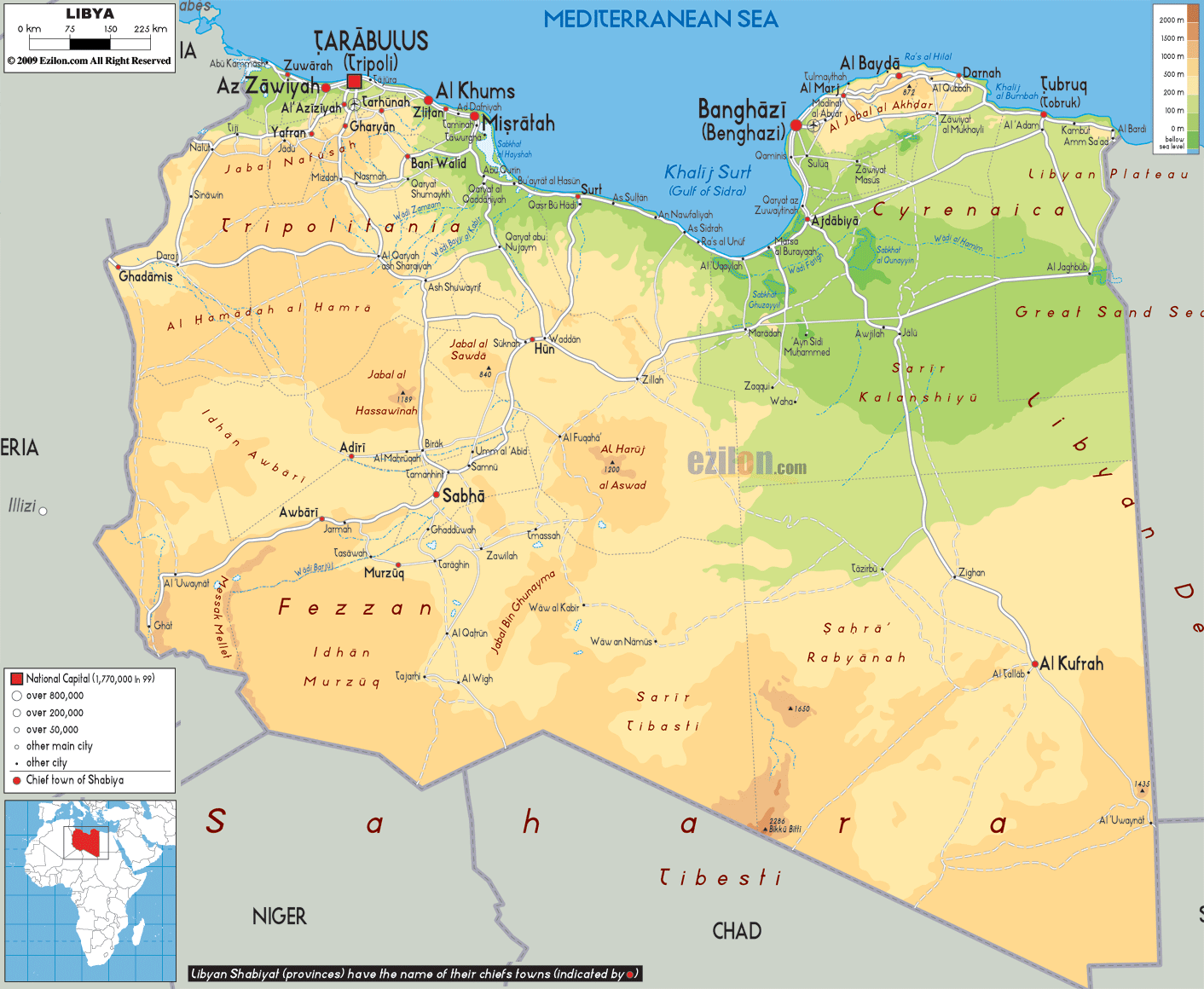
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Libya: A Geographic Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!