Navigating the Path to Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Path to Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Path to Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Path to Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning Maps

In the realm of education and skill development, navigating the vast landscape of knowledge can be daunting. Learning maps, also known as learning pathways or curriculum maps, provide a structured framework for navigating this complex terrain. They offer a visual representation of the learning journey, outlining the key concepts, skills, and knowledge required to achieve a specific learning objective. This article delves into the concept of learning maps, exploring their components, benefits, and applications.
Understanding Learning Maps: A Blueprint for Learning
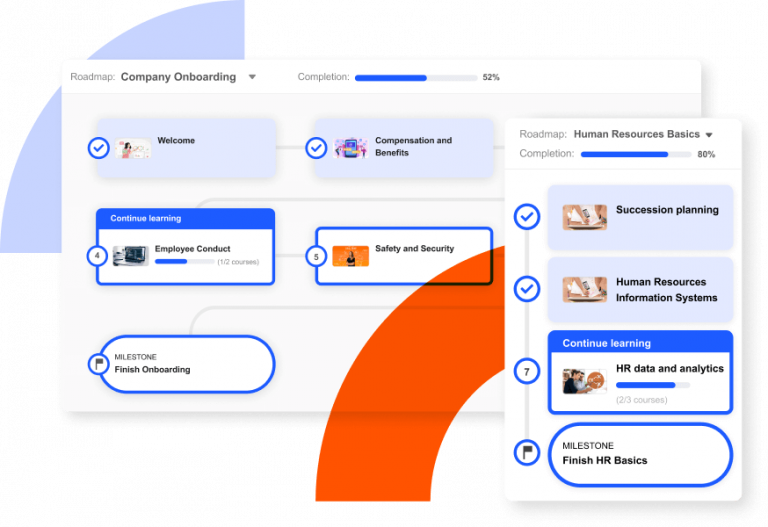
At its core, a learning map is a visual representation of a learning journey. It outlines the sequence of topics, skills, and assessments that learners need to progress towards a defined goal. Think of it as a road map for learning, guiding individuals through a clear and structured path.
Key Components of a Learning Map:
- Learning Objectives: Clearly defined goals that learners aim to achieve. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Learning Outcomes: The specific skills, knowledge, and abilities that learners will gain upon completion of the learning journey.
- Content Areas: The specific topics, concepts, and information that will be covered.
- Learning Activities: The various methods and strategies used to facilitate learning, such as lectures, discussions, group work, assignments, and assessments.
- Assessment Methods: The tools and strategies used to measure learner progress and achievement, including tests, quizzes, projects, and presentations.
- Resources: A list of relevant materials, including books, articles, websites, videos, and other learning resources.
- Timeline: A schedule or timeline indicating the duration of the learning journey and key milestones.
The Advantages of Utilizing Learning Maps:
- Clarity and Focus: Learning maps provide a clear understanding of the learning journey, ensuring learners are aware of the specific goals, content, and expectations.
- Enhanced Motivation: By visualizing the path to success, learning maps can motivate learners by providing a sense of progress and accomplishment.
- Improved Organization: Learning maps offer a structured framework, promoting organization and efficient time management.
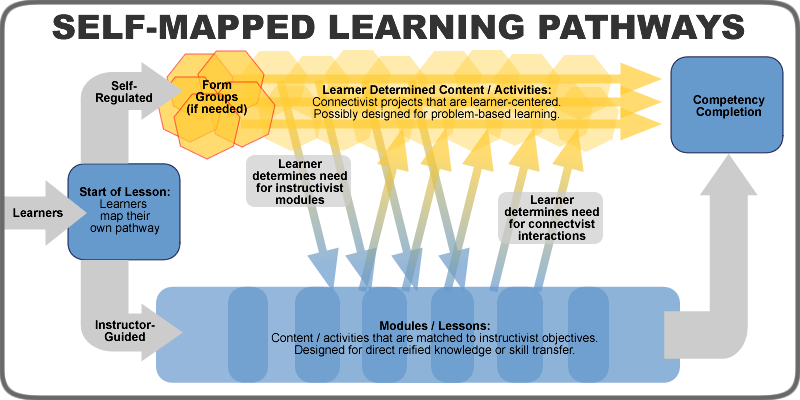
- Personalized Learning: Learning maps can be tailored to individual needs, accommodating different learning styles and pace.
- Effective Assessment: Learning maps integrate assessment methods, allowing for continuous monitoring of learner progress and providing feedback for improvement.
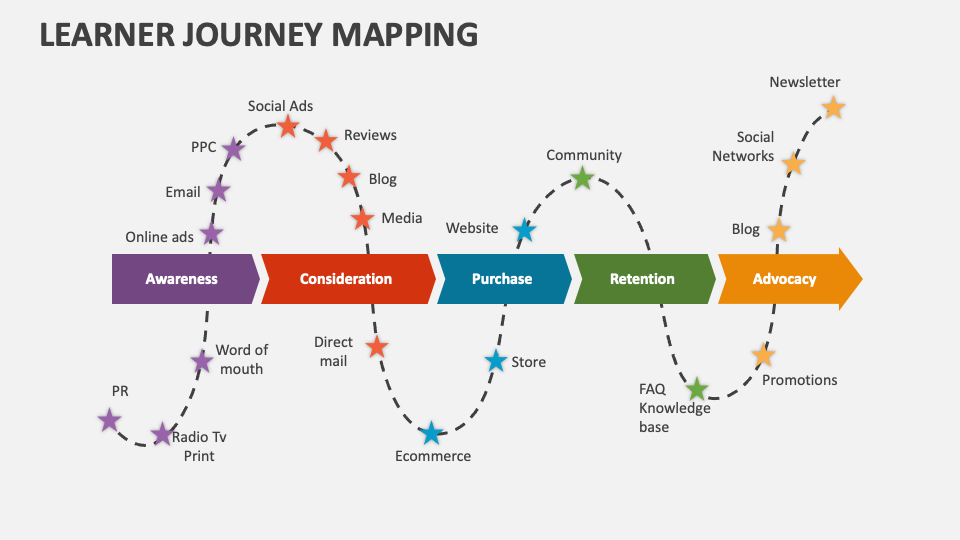
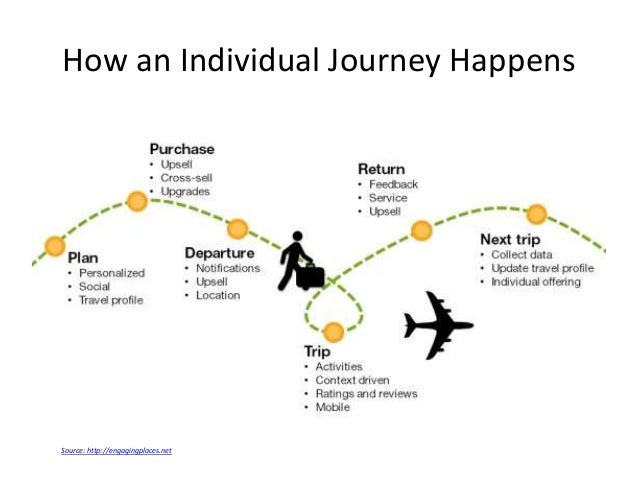
- Knowledge Transfer: Learning maps promote the transfer of knowledge and skills to real-world applications.
- Collaboration and Communication: Learning maps facilitate collaboration among learners, instructors, and stakeholders, promoting effective communication and shared understanding.
Applications of Learning Maps: A Wide Range of Possibilities
Learning maps find applications in diverse educational settings and professional contexts:
- Formal Education: Schools, colleges, and universities utilize learning maps to structure curricula, define learning objectives, and guide student progress.
- Professional Development: Organizations use learning maps to design training programs, skill development initiatives, and career advancement paths.
- Online Learning: Learning maps are essential tools in online learning platforms, providing learners with a clear roadmap for navigating online courses and modules.
- Self-Directed Learning: Individuals can create their own learning maps to guide their personal learning journeys, setting goals, identifying resources, and tracking progress.
FAQs Regarding Learning Maps
1. What are the key differences between learning maps and syllabuses?
While both learning maps and syllabuses provide information about a learning journey, they differ in their scope and focus. A syllabus typically outlines the course content, assignments, and grading criteria, while a learning map provides a more comprehensive visual representation of the learning journey, including learning objectives, outcomes, activities, and assessments.
2. How can I create a learning map?
Creating a learning map involves identifying the learning objective, outlining the key topics and skills, defining learning activities and assessments, and incorporating relevant resources. Tools like mind mapping software, online platforms, or even simple paper and pen can be used for visualization.
3. Can learning maps be used for all subjects and skill areas?
Yes, learning maps can be applied to any subject or skill area. They can be used for academic subjects, vocational training, professional development, personal growth, and more.
4. How can learning maps be used to support learners with diverse needs?
Learning maps can be adapted to cater to diverse learning needs. For example, visual learners may benefit from maps with clear visual representations, while auditory learners may prefer maps with audio components.
5. What are some best practices for using learning maps?
- Involve learners in the creation process: Encouraging learner participation in developing the map fosters ownership and engagement.
- Regularly review and update maps: As learning needs evolve, maps should be revised and updated to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
- Use clear and concise language: Maps should be easy to understand and navigate.
- Integrate diverse learning activities: Maps should incorporate a variety of learning activities to cater to different learning styles.
- Provide regular feedback: Feedback on learner progress should be provided throughout the journey, guided by the map.
Tips for Creating Effective Learning Maps:
- Start with a clear learning objective: Define the desired outcome of the learning journey.
- Break down the objective into smaller, manageable steps: Divide the learning journey into logical stages or modules.
- Identify the key skills and knowledge required: Determine the essential components of the learning journey.
- Choose appropriate learning activities: Select activities that align with learning styles and promote engagement.
- Incorporate assessment methods: Integrate assessments to track progress and provide feedback.
- Make it visually appealing: Use colors, graphics, and diagrams to enhance clarity and engagement.
- Provide resources and support: Include relevant materials, links, and contact information.
Conclusion: Empowering Learners Through Visual Guidance
Learning maps provide a valuable tool for navigating the complex world of learning. By offering a visual representation of the learning journey, they enhance clarity, motivation, and organization. Whether in formal education, professional development, or self-directed learning, learning maps empower individuals to take control of their learning, achieve their goals, and unlock their full potential. By embracing the power of visual guidance, we can create a more effective and engaging learning experience for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Path to Learning: A Comprehensive Guide to Learning Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!