Navigating the Wind River Range: A Cartographic Exploration
Related Articles: Navigating the Wind River Range: A Cartographic Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Wind River Range: A Cartographic Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Wind River Range: A Cartographic Exploration

The Wind River Range, a formidable mountain range in Wyoming, presents a complex landscape demanding careful navigation. Understanding its geography is crucial for safe and successful travel, whether for recreational pursuits, scientific research, or resource management. A comprehensive cartographic representation, therefore, serves as an indispensable tool. This analysis explores the multifaceted aspects of such representations, highlighting their utility and significance.
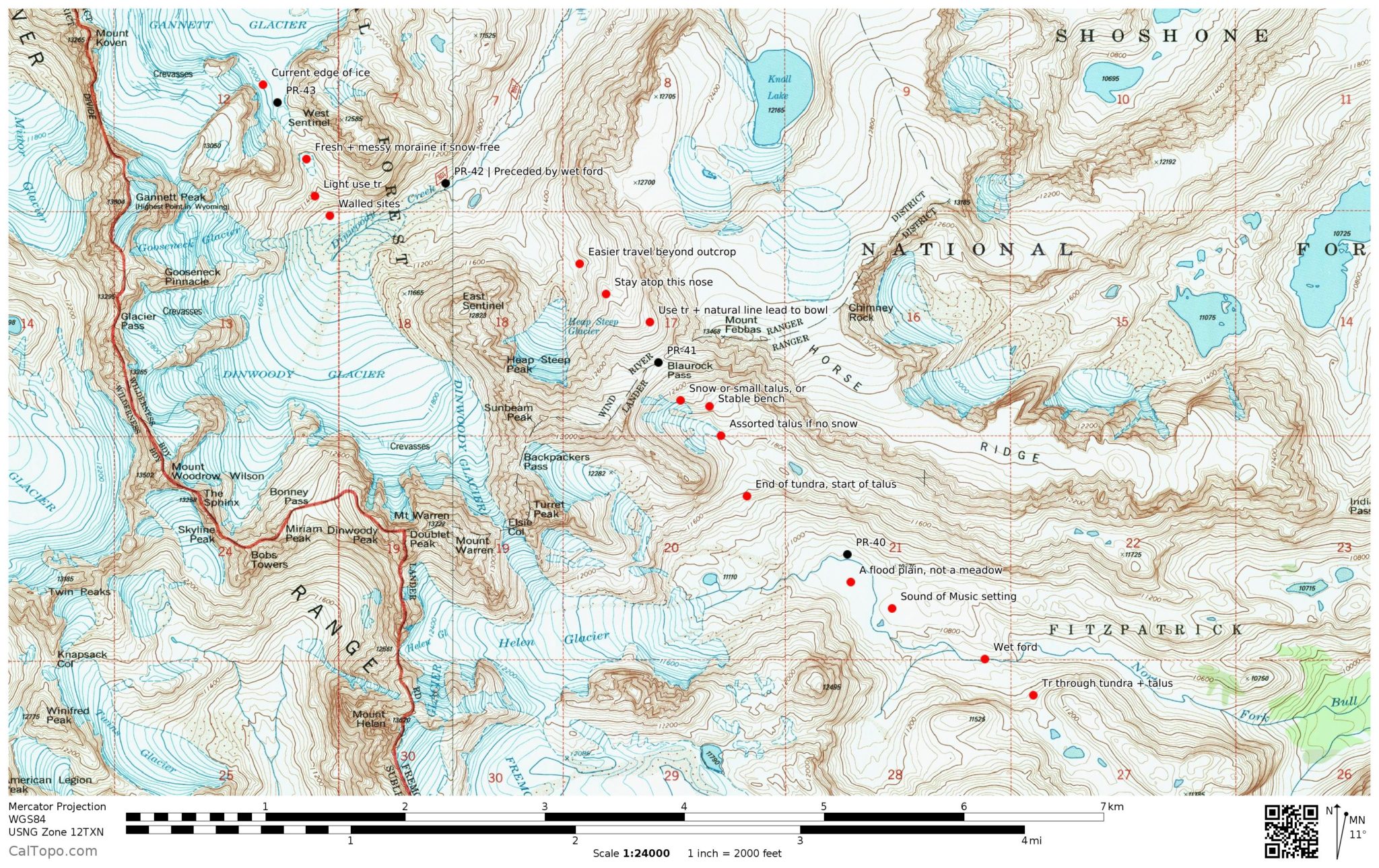
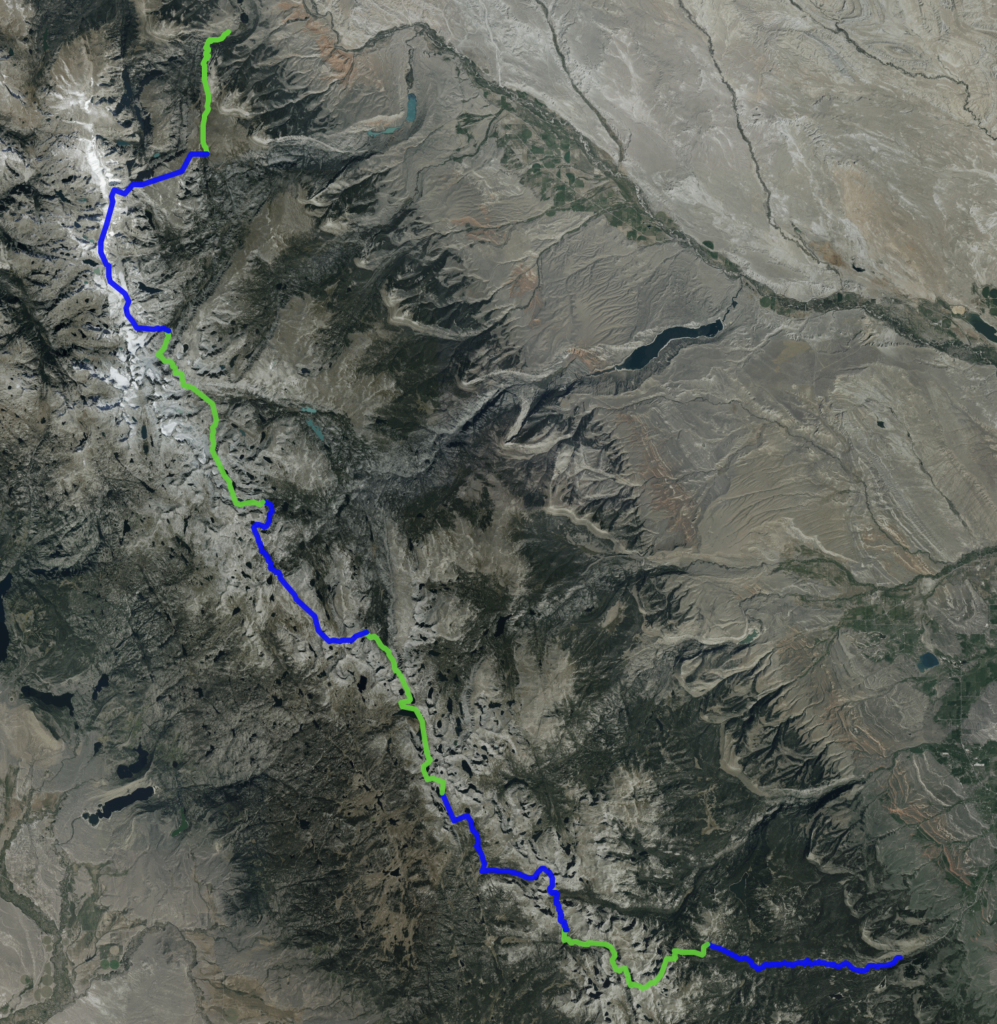
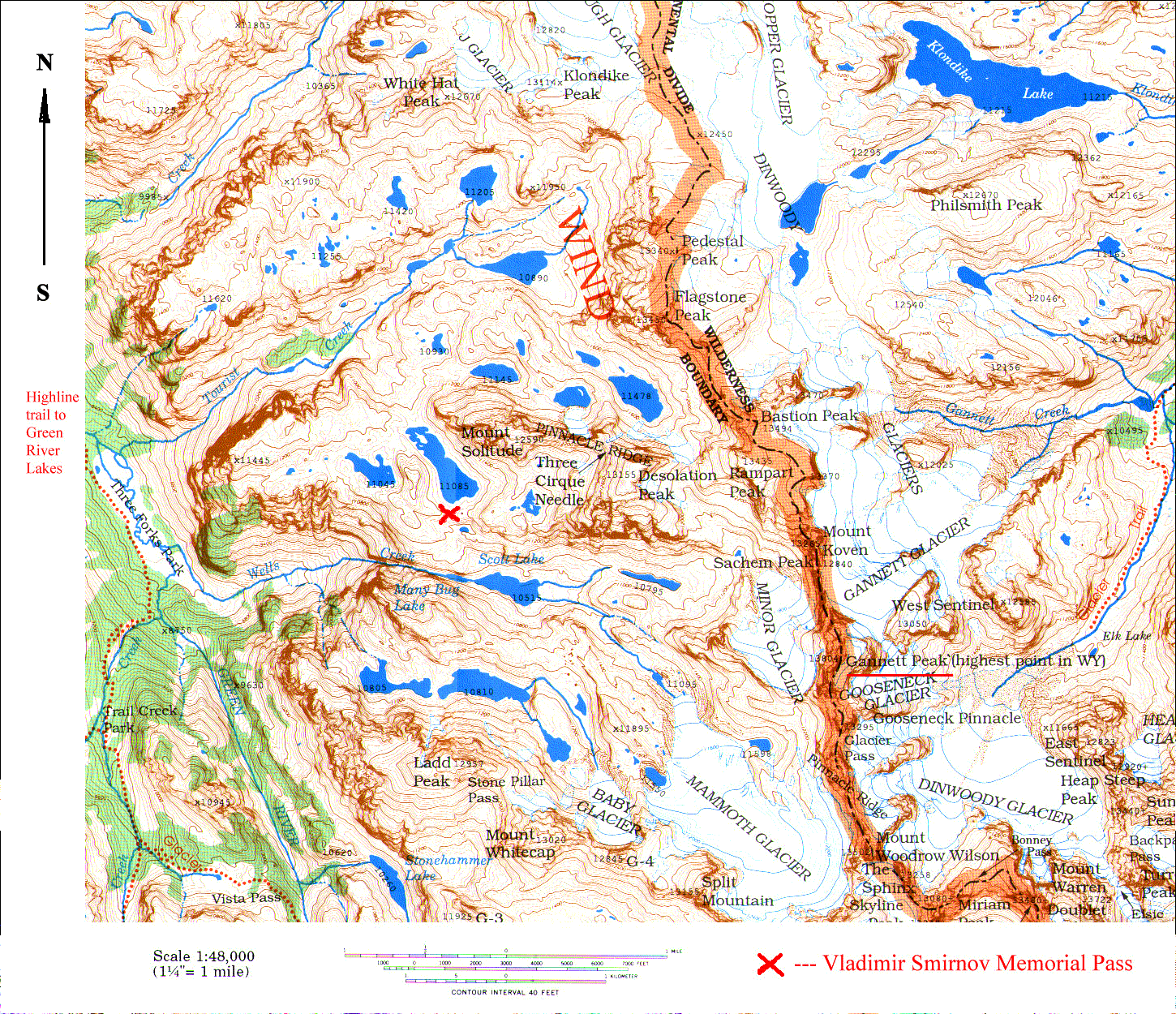
Topographic Detail and Elevation: The most fundamental aspect of any useful depiction is accurate topographic detail. High-resolution maps display elevation changes through contour lines, indicating the steepness of slopes, the presence of valleys, ridges, and passes. These contours, often coupled with shading or three-dimensional rendering, provide a visual representation of the terrain’s complexity. Accurate elevation data is critical for planning routes, assessing the difficulty of trails, and understanding potential hazards such as avalanche zones or rockfalls. Maps also typically incorporate spot elevations, providing precise altitude readings at specific points, further enhancing navigational accuracy.
Hydrographic Features: The Wind River Range is heavily influenced by its extensive network of waterways. Detailed representations accurately depict rivers, streams, lakes, and wetlands. This information is essential for identifying water sources, planning campsites near water, understanding potential flood risks, and determining the accessibility of certain areas. The depiction of drainage patterns reveals important information about the landscape’s hydrological processes and the potential for water-related challenges. Accurate depiction of seasonal changes in water levels is also crucial for effective planning.
Vegetation and Land Cover: The vegetation map layer provides valuable context for understanding the ecological characteristics of the range. Different vegetation types, such as forests, grasslands, and alpine tundra, are represented to illustrate the distribution of plant life. This information is relevant for understanding wildlife habitat, predicting potential hazards like wildfire risks, and planning recreational activities that minimize environmental impact. Land cover classification, encompassing features such as bare rock, snowfields, and glaciers, adds another level of detail, crucial for assessing the stability of the terrain and predicting potential hazards.
Trails and Access Points: Effective navigation relies heavily on the clear depiction of trails and access points. Maps should clearly distinguish between maintained trails, less-traveled paths, and unmaintained routes. The difficulty level of trails, along with distances and estimated travel times, should be indicated where possible. The location of trailheads, parking areas, and other access points is crucial for planning transportation logistics. The inclusion of waypoints and landmarks along the trails enhances navigational precision.
Geological Features: Understanding the underlying geology is vital for safe travel and resource management. Geological maps, integrated into the broader representation, identify rock formations, fault lines, and other geological features. This information is crucial for assessing potential hazards such as rockfalls and landslides. It is also essential for understanding the distribution of mineral resources and the overall geological context of the region.
Points of Interest: Comprehensive depictions often include points of interest, such as campsites, scenic overlooks, historical sites, and significant peaks. These points of interest can enhance the planning process and help users to identify potential destinations or areas of particular interest. Including information on permitted activities within specific zones contributes to responsible recreation and resource management.
Scale and Projection: The map’s scale significantly impacts its level of detail and usability. Large-scale maps provide high detail for smaller areas, suitable for detailed planning of shorter trips. Smaller-scale maps cover larger areas but provide less detail, useful for regional planning and overview. The map’s projection method influences the accuracy of distances and directions. Selecting an appropriate scale and projection is critical for the intended use.
Technological Advancements: Modern cartography utilizes Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and other technologies to create highly detailed and interactive maps. These digital representations often integrate multiple data layers, allowing users to customize their view and analyze specific aspects of the terrain. Online mapping platforms offer interactive features such as route planning, elevation profiles, and 3D visualizations, enhancing the user experience and navigational capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the best map for navigating the Wind River Range? The optimal map depends on the specific area and the intended activity. High-quality topographic maps published by the US Geological Survey (USGS) or reputable outdoor recreation companies are generally recommended. Digital maps with GPS integration are also increasingly popular.
-
Are there any dangers to be aware of when using these maps? While maps are invaluable tools, they are not infallible. Weather conditions, trail changes, and unforeseen hazards may not be accurately reflected. Always verify information with local sources and exercise caution.
-
How can I access these maps? USGS topographic maps can be purchased online or from outdoor retailers. Digital maps are readily available through online mapping platforms and dedicated outdoor navigation apps.
-
What information is most crucial to pay attention to on a Wind River Range map? Key elements include elevation contours, water sources, trail markings, and potential hazards such as steep slopes, avalanche zones, and unstable terrain.
-
Are there any legal restrictions on accessing certain areas of the Wind River Range? Permits or restrictions may apply to specific areas. Consult relevant land management agencies (e.g., the Bridger-Teton National Forest) before planning any trip.
Tips for Utilizing Maps of the Wind River Range
- Always carry a physical map as a backup, in case of electronic device failure.
- Verify map information with current trail reports and local sources.
- Plan routes carefully, considering elevation changes, water sources, and potential hazards.
- Inform someone of your itinerary and expected return time.
- Carry appropriate gear and supplies for the anticipated conditions.
- Be aware of changing weather conditions and adjust plans accordingly.
- Respect the environment and leave no trace.
Conclusion
Accurate and comprehensive cartographic representations are fundamental for safe and successful navigation within the challenging environment of the Wind River Range. Utilizing these tools effectively, combined with careful planning and preparation, enhances the experience of exploring this magnificent landscape while mitigating potential risks. The ongoing development and refinement of cartographic technologies continues to improve the accuracy and accessibility of information, thereby enhancing the ability to explore and understand this remarkable mountain range.
![727 :: Wind River Range South Map [Lander, Cirque of the Towers] by](https://store.avenza.com/cdn/shop/products/20210825113210TI00000727_0_1000px.jpg?v=1656683846u0026width=400)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Wind River Range: A Cartographic Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!