Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps
- 3.1 A Brief History of World Maps
- 3.2 Understanding the Basics of Map Projections
- 3.3 The Importance of Map Projections
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Types of World Maps
- 3.5 The Power of World Maps: Applications and Benefits
- 3.6 Frequently Asked Questions about World Maps
- 3.7 Tips for Using World Maps Effectively
- 3.8 Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of World Maps
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps

World maps, those ubiquitous representations of our planet, are more than just static images. They are powerful tools that shape our understanding of the world, influence our decisions, and inspire our imaginations. From ancient times to the digital age, maps have played a crucial role in human history, guiding explorers, connecting civilizations, and revealing the interconnectedness of our global community.
A Brief History of World Maps
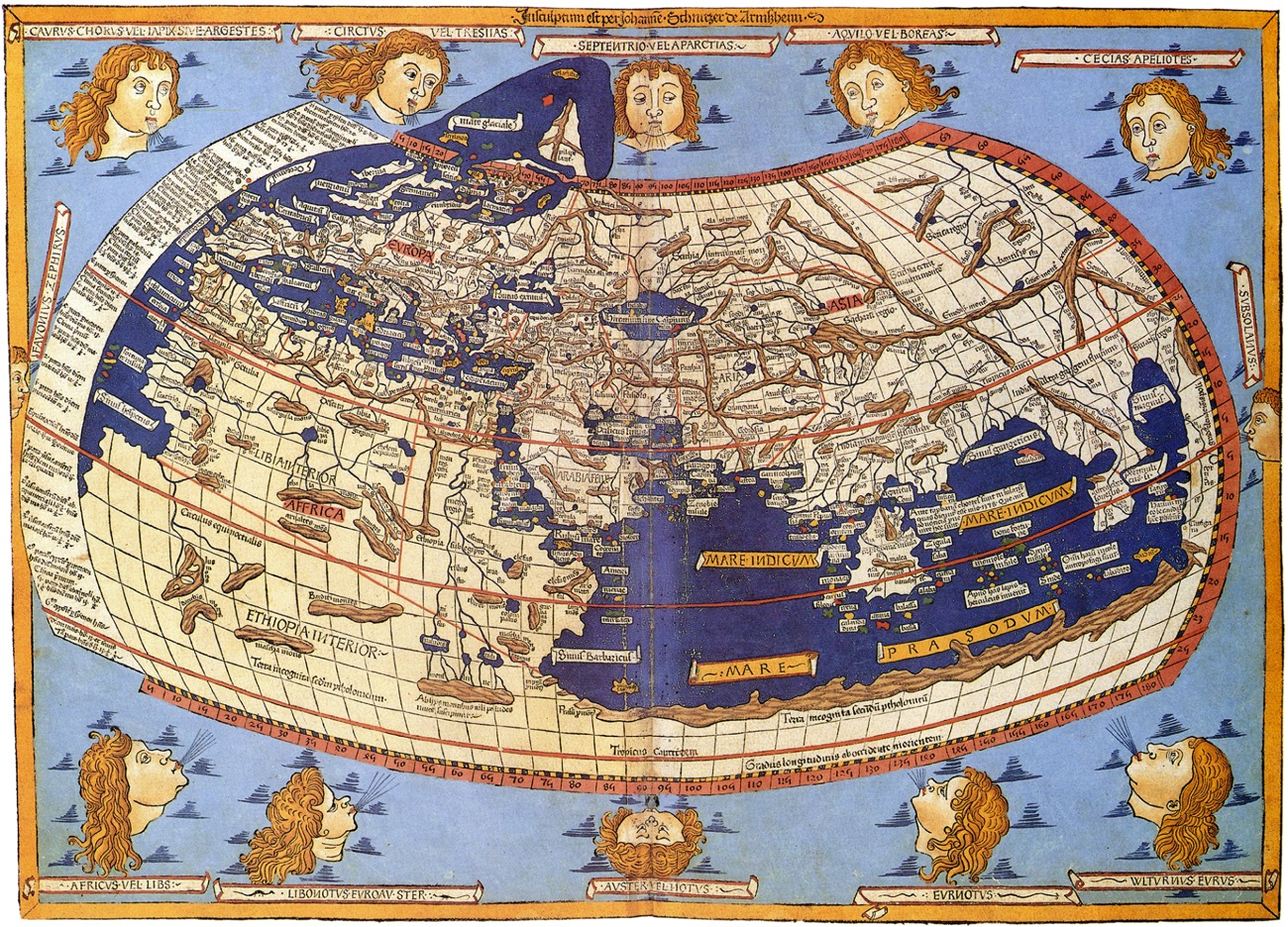
The earliest known world maps, dating back to ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Egyptians, were rudimentary representations of the known world, often reflecting a geocentric view. As knowledge expanded, so did the complexity of maps. The Greeks, with their advancements in astronomy and geography, created more accurate representations, including the famous map by Claudius Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD, which served as a standard for centuries.
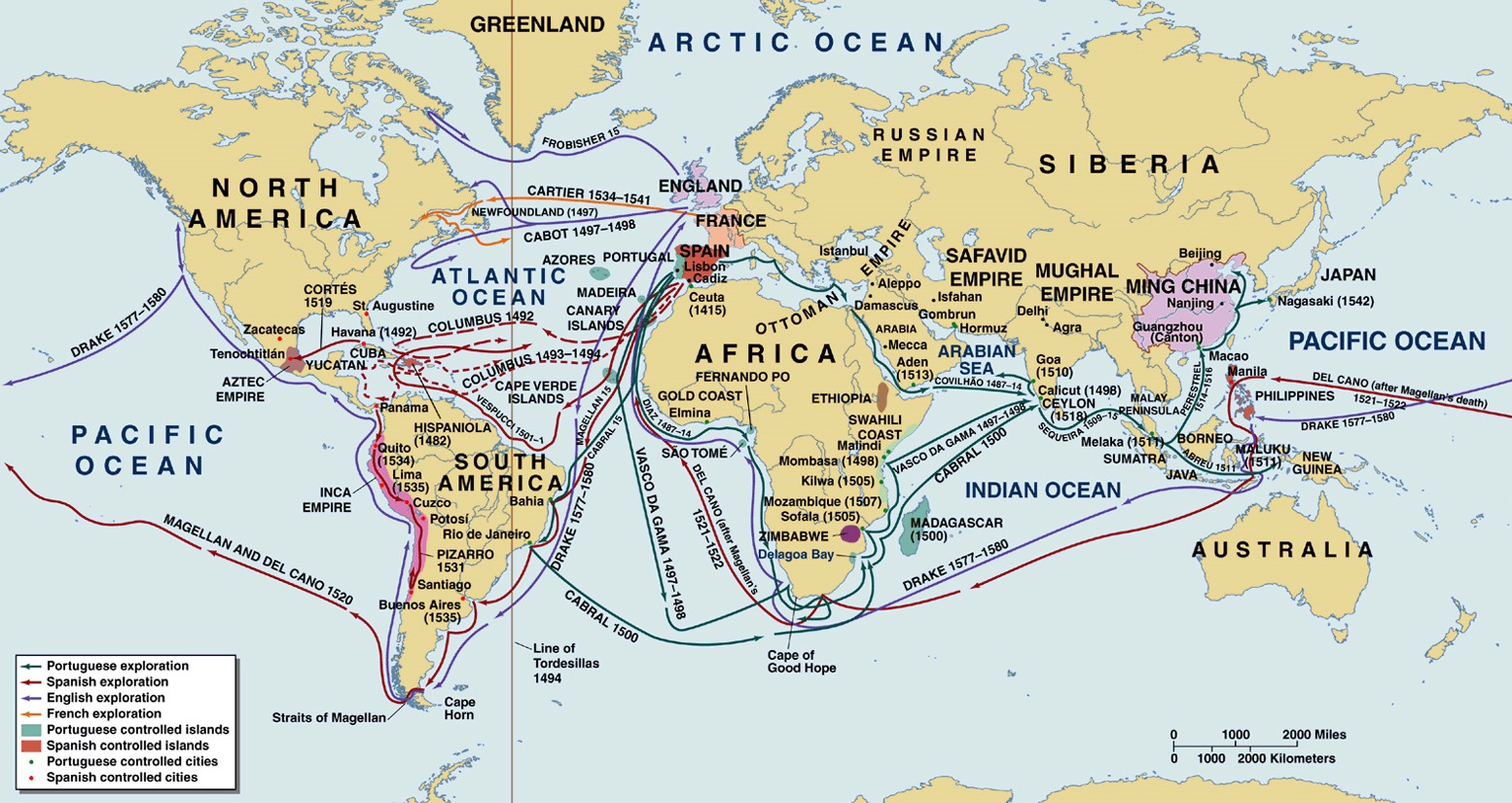
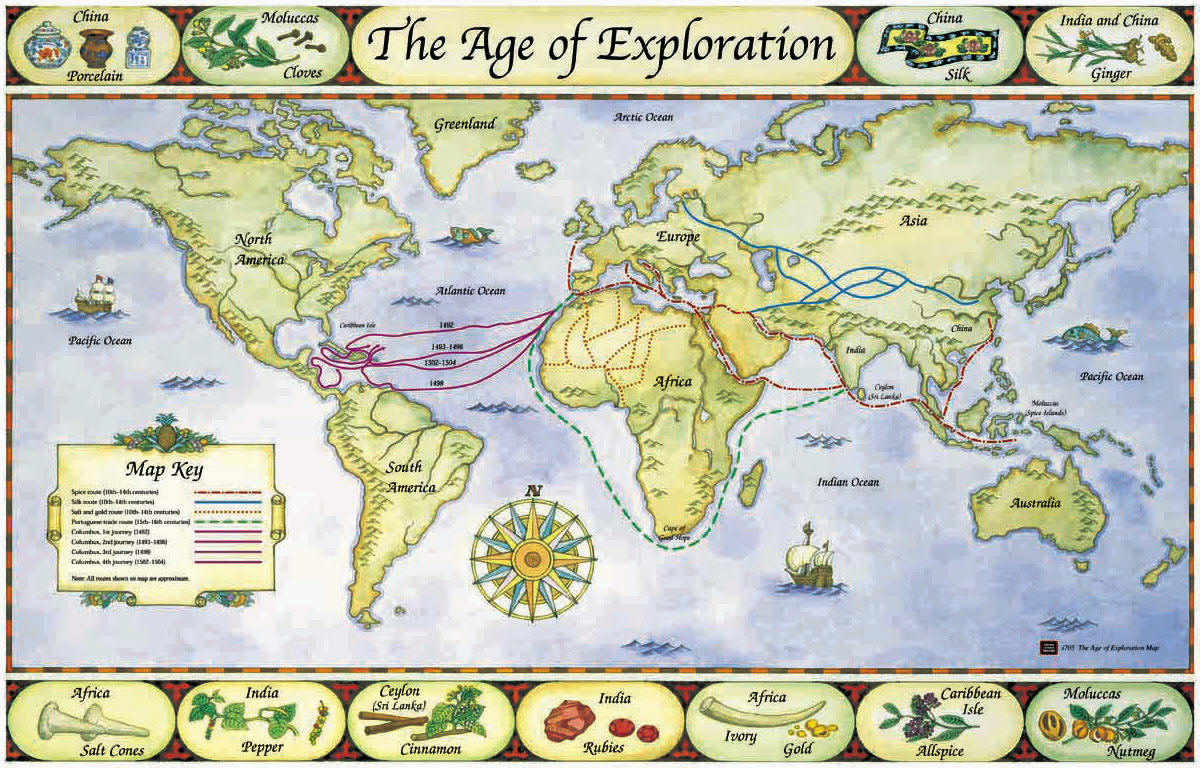
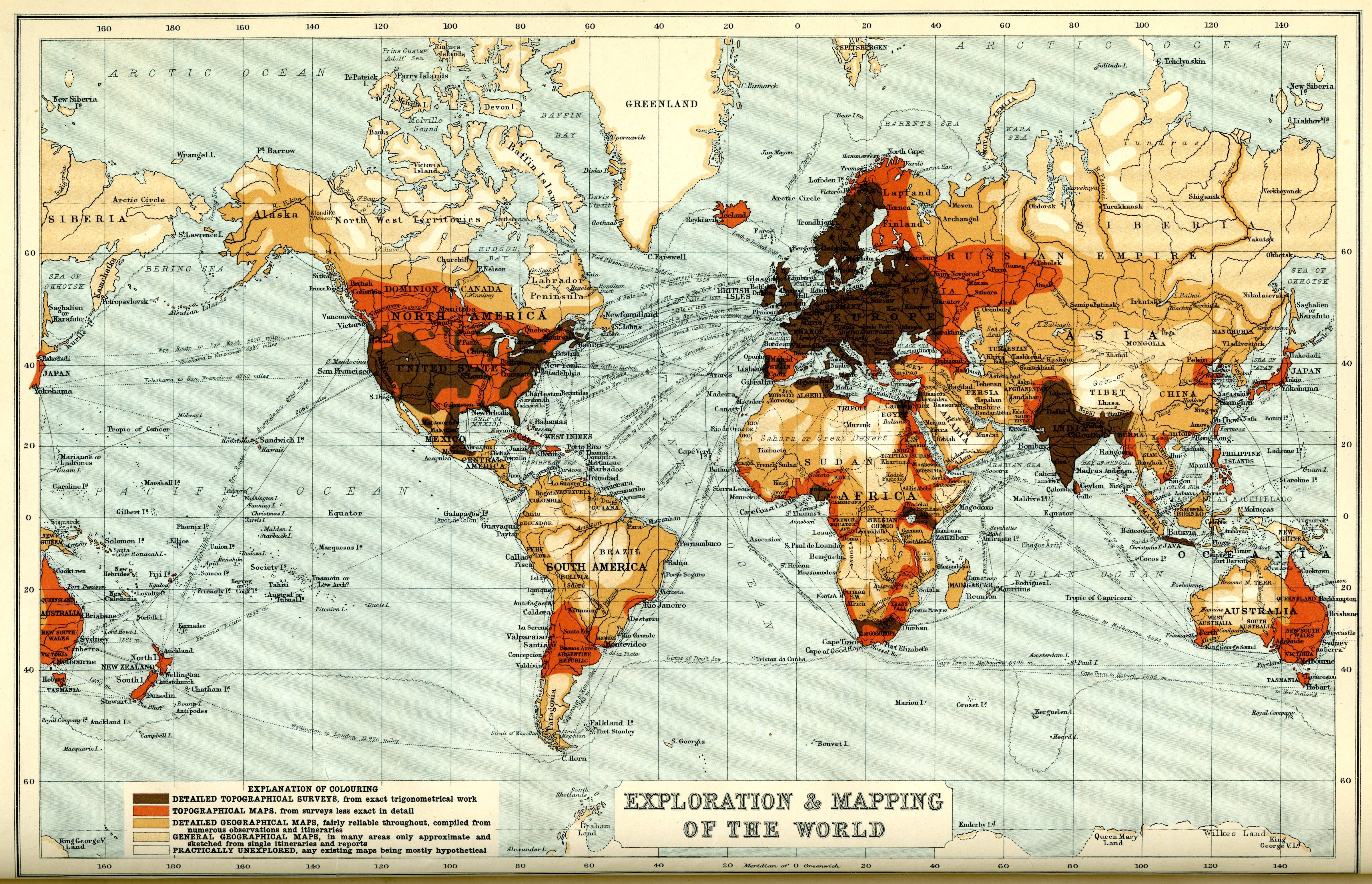
The Middle Ages saw the rise of mapmaking in the Islamic world, with scholars like al-Idrisi producing detailed and accurate maps. European exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries fueled a surge in mapmaking, leading to the development of more accurate projections and the inclusion of newly discovered lands. The Age of Enlightenment saw the emergence of scientific cartography, with maps becoming increasingly precise and detailed.
Understanding the Basics of Map Projections
World maps are not simply scaled-down versions of the Earth. Due to the Earth’s spherical shape, it is impossible to represent its surface accurately on a flat plane without distortion. This challenge led to the development of various map projections, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Common Map Projections:
- Mercator Projection: This cylindrical projection is widely used for navigation due to its preservation of angles, making it ideal for plotting courses. However, it significantly distorts areas, particularly at higher latitudes, making Greenland appear larger than Africa, despite being much smaller in reality.
- Gall-Peters Projection: This cylindrical projection aims to preserve area, meaning that the relative sizes of continents are accurately represented. However, it distorts shapes, making countries appear elongated.
- Robinson Projection: This compromise projection aims to minimize distortion by balancing area and shape preservation. It is commonly used for general-purpose maps.
- Winkel Tripel Projection: This projection balances area and shape distortion, making it suitable for world maps and atlases.
The Importance of Map Projections
The choice of map projection significantly impacts the way we perceive the world. Different projections emphasize different aspects of the Earth’s surface, leading to varying perceptions of size, shape, and distance. For example, the Mercator projection, while useful for navigation, can reinforce Eurocentric perspectives by exaggerating the size of northern countries.
Beyond the Basics: Types of World Maps
World maps are not limited to simple representations of continents and oceans. They can be used to visualize a wide range of data, including:
- Political Maps: These maps highlight the boundaries of countries, states, and other political entities.
- Physical Maps: These maps focus on the Earth’s physical features, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts.
- Thematic Maps: These maps use visual symbols and colors to represent specific data, such as population density, climate patterns, or resource distribution.
- Historical Maps: These maps depict the past, showing the evolution of boundaries, civilizations, or historical events.
The Power of World Maps: Applications and Benefits
World maps are essential tools for understanding and navigating our world. They play a crucial role in various fields, including:
- Navigation: Maps are fundamental for guiding ships, airplanes, and vehicles.
- Geography and Education: Maps are essential for teaching geography, history, and other subjects.
- Planning and Development: Maps are used for urban planning, resource management, and disaster preparedness.
- Research and Analysis: Maps help researchers visualize data, identify patterns, and draw conclusions.
- Communication and Storytelling: Maps are powerful tools for communicating information and telling stories about our world.
Frequently Asked Questions about World Maps
Q: What is the most accurate world map?
A: There is no single "most accurate" world map. All projections involve some level of distortion, and the best choice depends on the intended purpose. For example, a map designed for navigation will prioritize angle preservation, while a map for visualizing population density will emphasize area accuracy.
Q: Why are there different types of world maps?
A: Different map projections are designed to emphasize different aspects of the Earth’s surface, such as area, shape, or distance. The choice of projection depends on the specific application and the type of information being visualized.
Q: How do I choose the right world map for my needs?
A: Consider the purpose of the map, the type of information you want to represent, and the intended audience. For example, a general-purpose world map for educational purposes might use a compromise projection like the Robinson, while a map for navigation might utilize the Mercator projection.
Q: Are world maps still relevant in the age of GPS and online mapping?
A: While digital maps and GPS technology have revolutionized navigation, traditional world maps remain valuable tools for education, research, and understanding the global context. They provide a visual overview of the Earth’s geography, highlight global connections, and offer a historical perspective on our planet.
Tips for Using World Maps Effectively
- Consider the projection: Be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of different projections and choose the one that best suits your needs.
- Pay attention to scale: Understand the scale of the map and the level of detail it represents.
- Use multiple maps: Combine different types of maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of a particular topic or region.
- Look for reliable sources: Ensure that the maps you use are accurate and up-to-date.
- Use maps as a starting point for further exploration: World maps can spark curiosity and inspire further research and learning.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of World Maps
World maps are more than just static representations of our planet. They are powerful tools that shape our understanding of the world, influence our decisions, and inspire our imaginations. From ancient times to the digital age, maps have played a crucial role in human history, guiding explorers, connecting civilizations, and revealing the interconnectedness of our global community. As we continue to explore and understand our world, maps will remain essential tools for navigating, learning, and connecting with our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: An Exploration of World Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!