Terra Maps: Navigating the Digital Terrain of Data
Related Articles: Terra Maps: Navigating the Digital Terrain of Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Terra Maps: Navigating the Digital Terrain of Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Terra Maps: Navigating the Digital Terrain of Data
In the ever-expanding landscape of digital information, navigating complex datasets and extracting meaningful insights can be a daunting task. This is where terra maps emerge as a powerful tool, offering a visual and interactive representation of data, enabling users to explore, analyze, and understand intricate relationships within vast datasets.
Understanding Terra Maps: A Visual Journey Through Data
Terra maps, also known as data landscapes, are a visual representation of data, often presented as a three-dimensional terrain. The height of the terrain reflects the value of the data, creating a visual landscape that highlights peaks and valleys, representing high and low values respectively. This approach provides a powerful way to visualize complex datasets and identify trends, outliers, and patterns that might be difficult to discern through traditional methods.
Beyond Visualization: The Power of Interactivity
Terra maps go beyond simple visualization, offering interactive features that enhance exploration and analysis. Users can zoom in and out of the terrain, rotate the map, and apply various filters to focus on specific data points or segments. This interactive approach empowers users to delve deeper into the data, uncovering hidden relationships and gaining a more nuanced understanding of the underlying trends.
Applications of Terra Maps: From Business Intelligence to Scientific Discovery
The versatility of terra maps makes them applicable across a wide range of disciplines and industries. Here are some prominent examples:
1. Business Intelligence:
- Sales Analysis: Identifying high-performing sales regions, product categories, or customer segments.
- Market Research: Understanding customer demographics, preferences, and buying behavior.
- Risk Management: Visualizing potential risks and opportunities within a business.
2. Healthcare:
- Disease Surveillance: Tracking the spread of infectious diseases and identifying hotspots.
- Patient Outcomes: Analyzing patient data to identify factors influencing treatment success.
- Drug Discovery: Visualizing drug efficacy and identifying potential targets for new treatments.
3. Finance:
- Investment Analysis: Identifying profitable investment opportunities and managing portfolio risk.
- Fraud Detection: Detecting unusual patterns in financial transactions that may indicate fraudulent activity.
- Market Forecasting: Predicting future market trends based on historical data.
4. Environmental Science:
- Climate Change Analysis: Visualizing the impact of climate change on weather patterns and ecosystems.
- Pollution Monitoring: Tracking air, water, and soil pollution levels and identifying sources.
- Species Distribution: Mapping the distribution of plant and animal species and understanding their habitat preferences.
5. Social Sciences:
- Public Opinion Analysis: Visualizing public sentiment towards social issues and political events.
- Urban Planning: Understanding population density, traffic patterns, and resource distribution within cities.
- Social Mobility: Analyzing social mobility trends and identifying factors contributing to inequality.
Benefits of Terra Maps: A Clearer View of Data
The use of terra maps offers a multitude of benefits, including:
- Enhanced Data Understanding: Visualizing complex datasets in an intuitive and engaging way, making it easier to identify patterns and trends.
- Improved Decision-Making: Providing a clearer and more comprehensive view of data, leading to more informed and data-driven decisions.
- Increased Collaboration: Facilitating collaboration among team members by providing a shared understanding of the data and its implications.
- Faster Insights: Accelerating the process of data analysis and interpretation, leading to faster insights and quicker decision-making.
- Improved Communication: Communicating complex data insights effectively to stakeholders with limited technical expertise.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What types of data are suitable for terra maps?
A: Terra maps are well-suited for both numerical and categorical data. Numerical data can be represented by the height of the terrain, while categorical data can be visualized using different colors or textures.
Q: What software tools can be used to create terra maps?
A: Several software tools can be used to create terra maps, including Tableau, Power BI, Qlik Sense, and R. These tools offer a range of features for data visualization, analysis, and interaction.
Q: How can I choose the appropriate data variables for a terra map?
A: The choice of data variables depends on the specific research question or business problem you are trying to address. It is essential to select variables that are relevant to the analysis and provide meaningful insights.
Q: What are some common challenges in creating and using terra maps?
A: Some challenges include selecting the right data variables, ensuring data quality, and interpreting the visualized data accurately. It is important to have a good understanding of the data and the context in which it is being used.
Tips for Effective Terra Map Creation and Usage:
- Clear Objectives: Define the specific research question or business problem you are trying to address.
- Data Preparation: Clean and prepare the data to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Variable Selection: Carefully select variables that are relevant to the analysis and provide meaningful insights.
- Visualization Techniques: Experiment with different visualization techniques to find the most effective representation for the data.
- Interactive Features: Utilize interactive features to enhance exploration and analysis, allowing users to delve deeper into the data.
- Context and Interpretation: Provide context and interpretation for the visualized data, ensuring that users understand the significance of the findings.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Data Visualization
Terra maps offer a powerful and versatile approach to data visualization, providing a clear and intuitive representation of complex datasets. By leveraging the benefits of interactive exploration and analysis, terra maps empower users to gain deeper insights, make informed decisions, and communicate data effectively. As data continues to grow in volume and complexity, terra maps will play an increasingly important role in navigating the digital terrain of information and extracting meaningful insights from the vast sea of data.



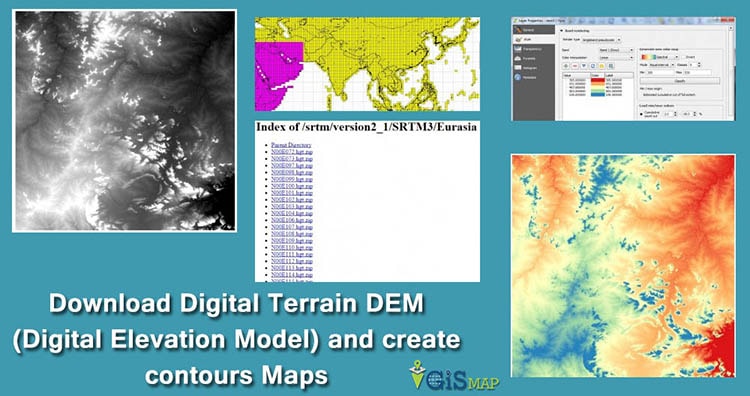

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Terra Maps: Navigating the Digital Terrain of Data. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!