The Power of Visualization: Unveiling Insights with Dot Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Visualization: Unveiling Insights with Dot Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Visualization: Unveiling Insights with Dot Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Visualization: Unveiling Insights with Dot Maps
In the realm of data visualization, the dot map stands as a powerful tool for conveying information in a clear, concise, and visually compelling manner. Its simplicity belies its effectiveness in revealing patterns, trends, and spatial relationships within datasets, making it a valuable asset for various disciplines.
Understanding the Essence of Dot Maps
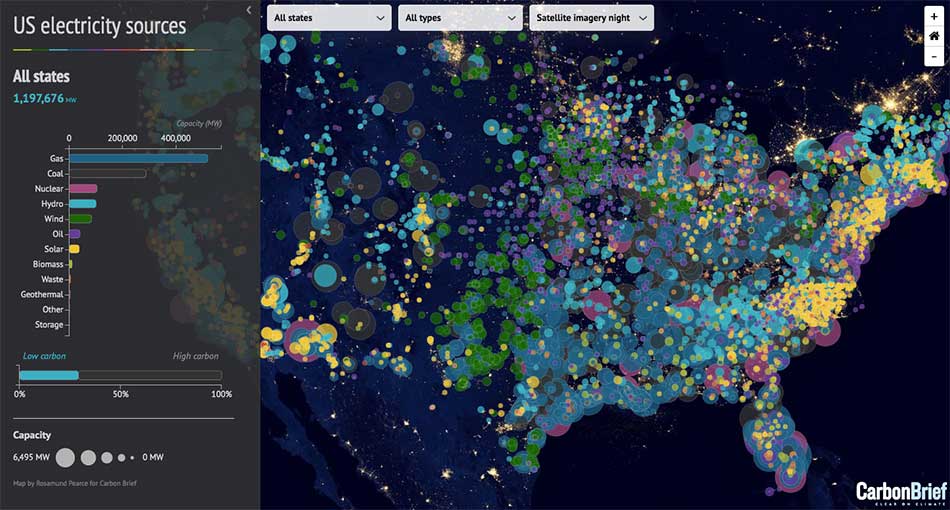
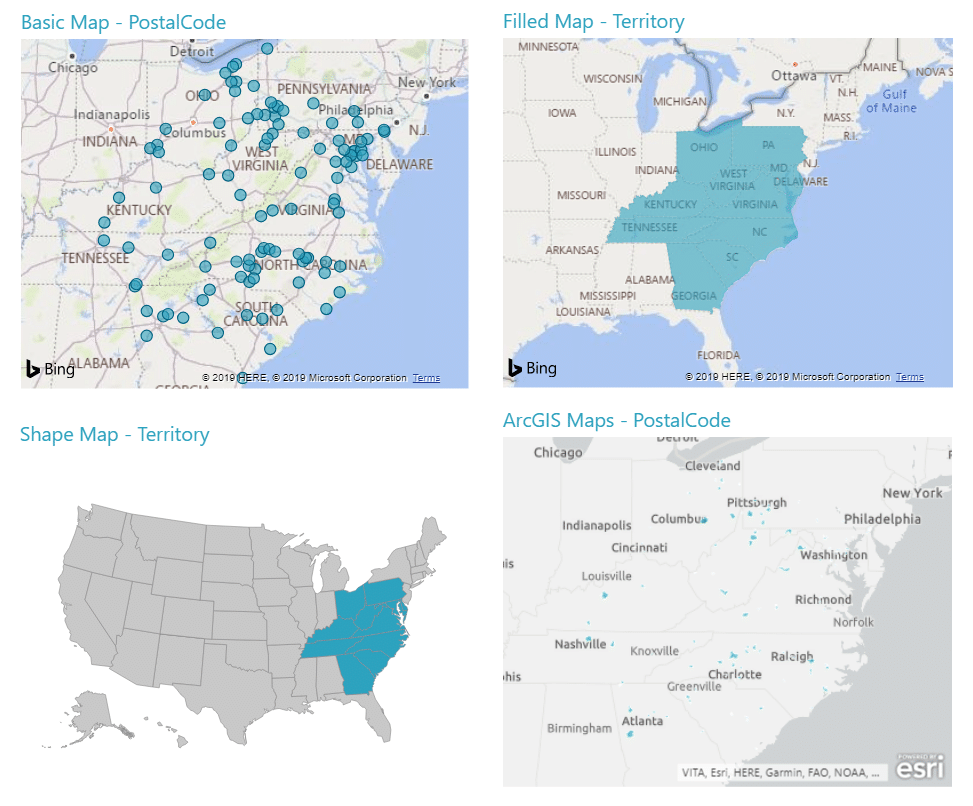
At its core, a dot map is a type of thematic map that utilizes dots or circles to represent data points. Each dot corresponds to a specific location, with its size or color often reflecting the magnitude of the data value associated with that location. This method allows for a straightforward representation of spatial distribution, density, and concentration of data points.
Key Features and Applications
Dot maps excel in showcasing various data types, including:
- Population Density: Visualizing the distribution of population across a region, highlighting areas with high or low population concentrations.
- Disease Prevalence: Mapping the occurrence of diseases, enabling the identification of hotspots and potential outbreaks.
- Business Locations: Representing the geographical spread of businesses, facilitating market analysis and competitor identification.
- Crime Rates: Visualizing crime patterns, aiding in crime prevention and resource allocation.
- Environmental Data: Mapping pollution levels, resource distribution, or biodiversity hotspots, informing environmental management and policy decisions.
Advantages and Benefits of Dot Maps
The effectiveness of dot maps stems from several key advantages:
- Clarity and Simplicity: Their straightforward design makes them easily interpretable, even for those unfamiliar with complex data representations.
- Visual Impact: The use of dots creates a visually engaging and memorable representation of data, facilitating understanding and retention.
- Spatial Insights: Dot maps effectively convey spatial relationships, allowing for the identification of clusters, outliers, and patterns that might be missed in tabular data.
- Data Comparison: By utilizing color or size variations, dot maps can effectively compare data values across different locations, revealing significant differences or trends.
- Dynamic Visualization: Interactive dot maps allow users to explore data in real-time, zooming in on specific areas, filtering by criteria, and gaining deeper insights.
Construction and Customization
Creating a dot map involves a few crucial steps:
- Data Acquisition: Collect the relevant data for the desired geographic area, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
- Data Preparation: Clean and format the data, assigning appropriate values to each location.
- Map Selection: Choose a suitable base map that aligns with the scale and geographic scope of the data.
- Dot Representation: Determine the size, color, and shape of the dots to effectively convey the data values.
- Legend and Labels: Include a clear legend explaining the meaning of dot sizes, colors, or shapes, and provide appropriate labels for geographic features.
Customization options can further enhance the effectiveness of dot maps:
- Color Gradients: Employing a color gradient can visually represent data ranges, allowing for easy identification of high and low values.
- Dot Clustering: Grouping dots in areas of high density can improve readability and prevent visual clutter.
- Interactive Features: Incorporating zoom, pan, and filtering capabilities allows for dynamic data exploration and deeper analysis.
FAQs on Dot Maps
Q: What are the limitations of dot maps?
A: Dot maps, while powerful, have some limitations:
- Data Granularity: They may not be suitable for representing data with very fine granularity, as overlapping dots can obscure individual data points.
- Data Complexity: Representing highly complex data with multiple variables might require alternative visualization techniques.
- Scale Issues: Mapping large datasets with millions of data points can lead to visual clutter and difficulty in discerning individual locations.
Q: How can I choose the appropriate size and color for my dots?
A: The choice of size and color depends on the nature of the data and the desired emphasis. Larger dots represent higher values, while colors can be used to distinguish categories or emphasize specific data ranges.
Q: Can dot maps be used for time series data?
A: Yes, dot maps can be used for time series data by creating a series of maps for different time periods, allowing for the visualization of changes in spatial distribution over time.
Tips for Effective Dot Map Creation
- Choose the Right Scale: Select a map scale that effectively represents the data and avoids excessive clutter.
- Use Clear and Concise Labels: Label geographic features and key data points for easy interpretation.
- Employ a Consistent Color Scheme: Use a color scheme that is both visually appealing and conveys the data effectively.
- Avoid Overcrowding: Use clustering techniques or adjust dot size to prevent visual clutter in areas of high density.
- Include a Clear Legend: Ensure the legend accurately explains the meaning of dot size, color, or shape.
Conclusion
Dot maps offer a versatile and effective method for visualizing spatial data, providing valuable insights into distribution, density, and trends. Their simplicity, clarity, and visual impact make them a powerful tool for researchers, policymakers, and anyone seeking to understand and communicate spatial information. By leveraging the advantages of dot maps and incorporating best practices for their creation, users can unlock the full potential of this visualization technique and gain a deeper understanding of the world around them.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Visualization: Unveiling Insights with Dot Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!