Visualizing Data on the United States: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartographic Representation
Related Articles: Visualizing Data on the United States: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartographic Representation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data on the United States: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartographic Representation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Data on the United States: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartographic Representation

The United States, with its vast geographical expanse and diverse population, presents a complex landscape for data visualization. Effectively communicating information about this nation requires sophisticated cartographic techniques. Representing data geographically on a US map allows for a powerful and intuitive understanding of patterns, trends, and disparities across regions. This analysis explores the various methods employed and their applications, highlighting the crucial role these techniques play in informing decision-making across numerous sectors.
Methods of Geographic Data Representation:
Several methods exist for displaying data geographically on a US map, each with its own strengths and weaknesses depending on the type of data and the intended audience. These include:
-
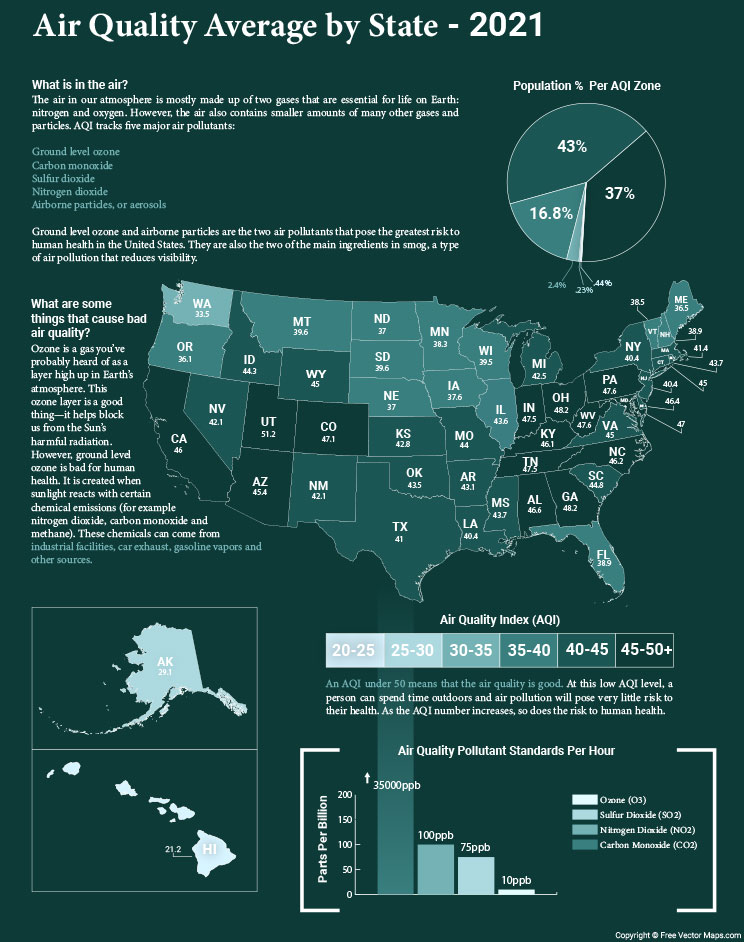
Choropleth Maps: These maps use color shading or patterns to represent data values across different geographic units, such as states or counties. Darker shades typically indicate higher values, while lighter shades represent lower values. Choropleth maps are effective for showing spatial variations in data like population density, income levels, or voting patterns. However, they can be misleading if the geographic units vary significantly in size or population. A large, sparsely populated state might appear to have a low value simply due to its size, rather than its actual data density.
-
Proportional Symbol Maps: These maps use symbols of varying sizes to represent data values at specific locations. Larger symbols indicate higher values, while smaller symbols indicate lower values. This method is effective for visualizing data points with distinct locations, such as the number of hospitals in each city or the magnitude of earthquakes at their epicenters. However, symbol overlap can become a problem in densely populated areas, hindering clarity.
-
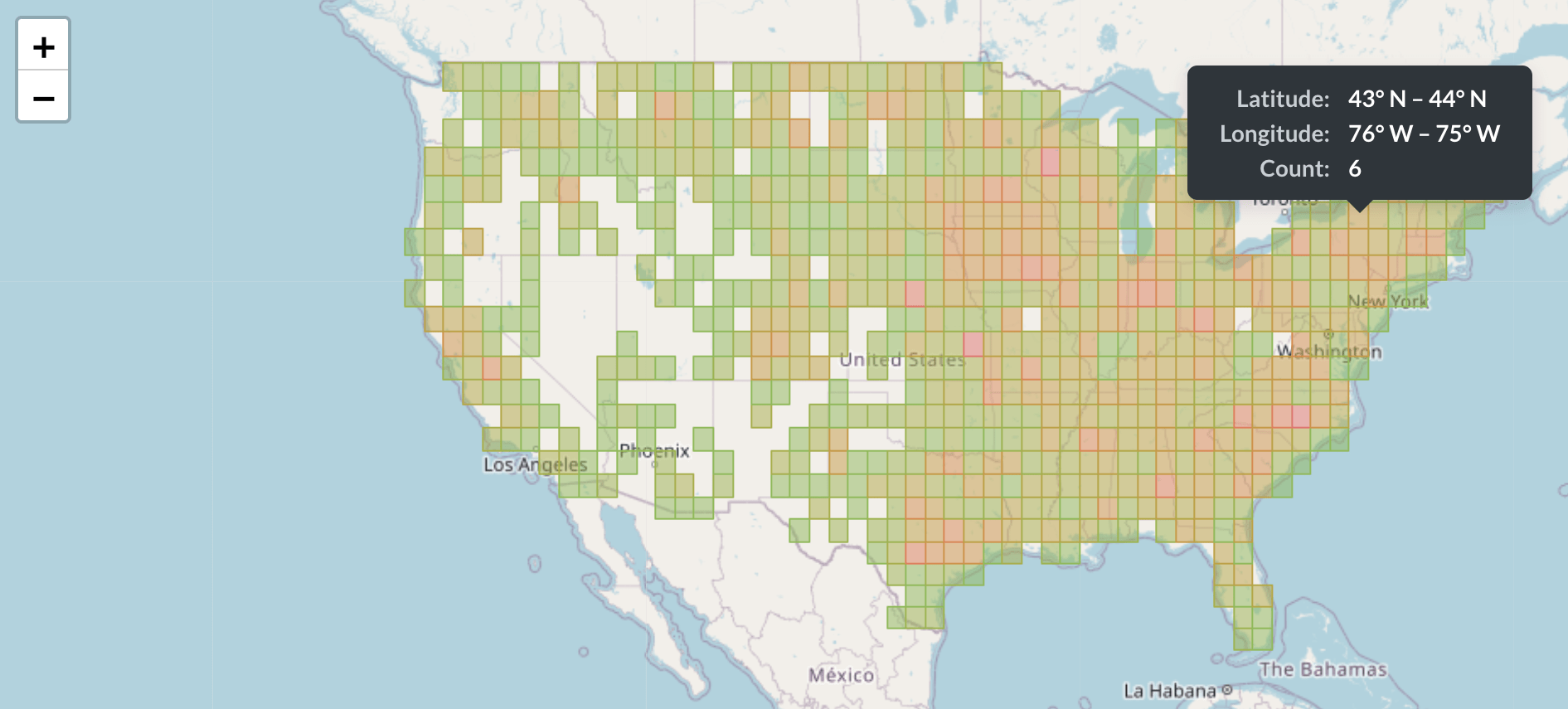
Dot Density Maps: Similar to proportional symbol maps, dot density maps use dots to represent data values. Each dot represents a certain number of units, and the concentration of dots indicates the density of the data. This method is particularly useful for visualizing large datasets where individual data points are less important than overall density. For example, a dot density map could effectively represent population distribution across the country. However, the map’s clarity can be compromised if the dot density becomes too high.
-
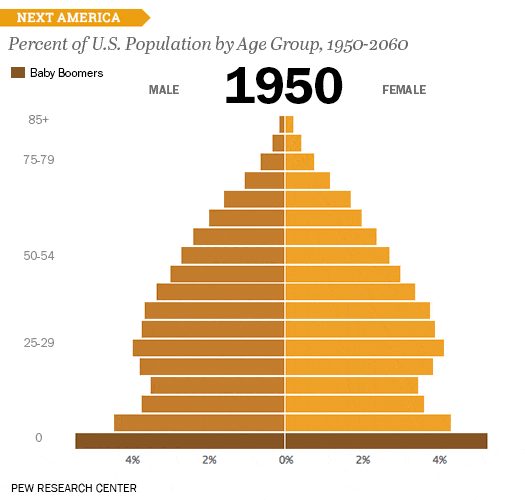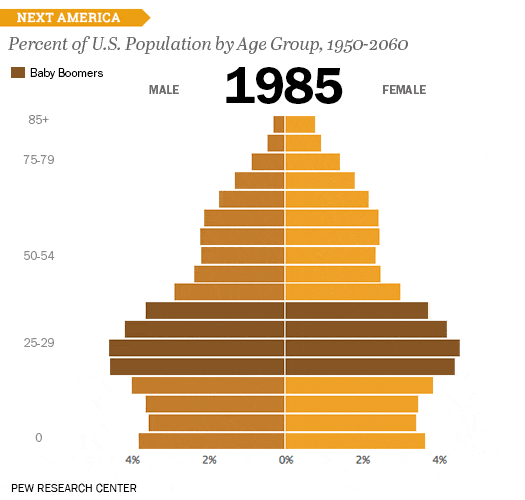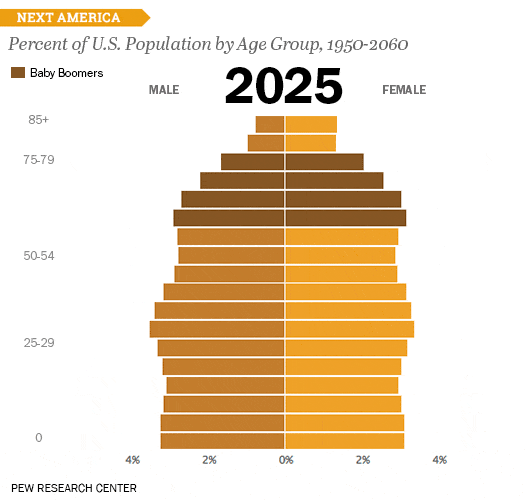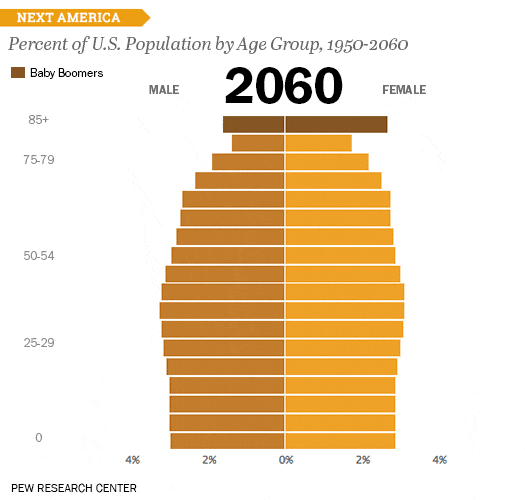
Isopleth Maps: These maps use lines to connect points of equal value, creating contours that show the spatial distribution of a continuous phenomenon. Isopleth maps are particularly useful for representing data like temperature, elevation, or precipitation. However, they require a substantial amount of data and can be complex to interpret if many contours are present.
-
Cartogram: Cartograms distort the geographical shapes of states or counties to reflect the magnitude of a particular variable. For example, a cartogram showing population might make populous states like California and Texas appear much larger than their actual geographical size, while less populated states appear smaller. This method allows for a clear visual representation of the relative importance of each area regarding the chosen variable but sacrifices geographical accuracy.
Applications Across Diverse Fields:
The application of these cartographic techniques extends across numerous fields, including:
- Public Health: Mapping disease outbreaks, identifying health disparities, and tracking vaccination rates.
- Environmental Science: Visualizing pollution levels, monitoring deforestation, and analyzing climate change impacts.
- Economics: Showing income inequality, analyzing market trends, and mapping economic activity.
- Politics: Representing election results, visualizing voter demographics, and analyzing political polarization.
- Urban Planning: Mapping population density, identifying areas in need of infrastructure development, and analyzing traffic patterns.
- Business: Identifying target markets, analyzing sales data, and optimizing supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What software is best suited for creating US maps with data visualization? Several software packages are available, including ArcGIS, QGIS (open-source), and various mapping tools within spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets. The optimal choice depends on the complexity of the data and the user’s technical skills.
-
How can data accuracy be ensured when creating these maps? Data accuracy is paramount. Reliable data sources must be used, and data cleaning and validation processes should be implemented to minimize errors. Furthermore, the chosen mapping method should be appropriate for the data type and should be clearly explained to avoid misinterpretations.
-
What are the ethical considerations involved in creating and presenting these maps? Maps can be powerful tools, but they can also be misused to perpetuate biases or mislead the audience. Ethical considerations include ensuring data transparency, avoiding misleading visualizations, and acknowledging limitations in the data or the mapping method.
Tips for Effective Data Visualization on US Maps:
- Choose the appropriate mapping method: The selected method should accurately represent the data and be easily understood by the intended audience.
- Use a clear and consistent legend: The legend should clearly explain the meaning of colors, symbols, or patterns used on the map.
- Maintain geographical accuracy: Unless using a cartogram, maintain the geographical integrity of the map.
- Keep the map simple and uncluttered: Avoid overwhelming the audience with too much information.
- Provide context: Include a title, source information, and any necessary explanations.
Conclusion:
Representing data geographically on US maps is a crucial tool for understanding and communicating complex information about the nation. By selecting the appropriate mapping method and adhering to best practices, data visualization can effectively reveal patterns, trends, and disparities, informing decision-making across various sectors and fostering a deeper understanding of the United States’ diverse landscape. The continued development and application of these techniques will remain essential for navigating the challenges and opportunities facing the country.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data on the United States: A Comprehensive Guide to Cartographic Representation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!